Table of Contents
If you are a trader, you know how sometimes some assets can achieve 100 pips in just a few hours. However, some currency pairs oscillate around the same price for several days. For example, one-time EURCHF was several days only in the 15 pips range. Based on several years of time-span research, this article will describe which forex pairs move the most and which pairs the least.
What is volatility in the forex market?
Forex volatility measures overall price fluctuations over a specific time and how rapidly a market’s prices change in the forex market. Volatility is merely the standard deviation of returns. High-liquid assets like significant forex pairs have low volatility and move in smaller increments.
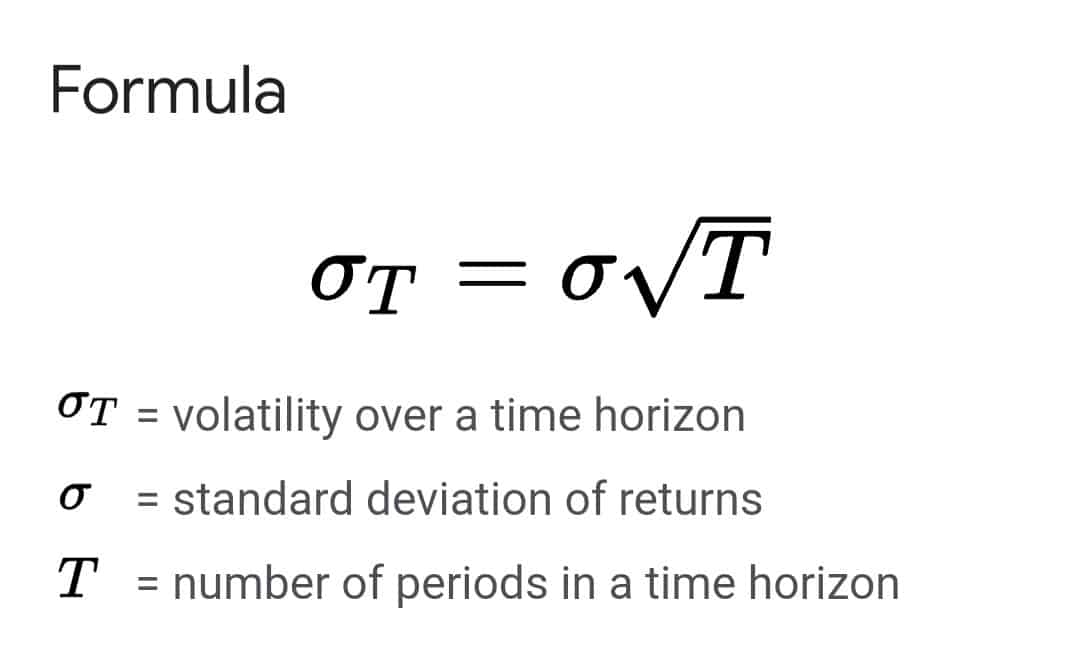
Difference between risk and volatility
Volatility is not always bad because it can be an opportunity in trading. However, there is a difference between risk and volatility. Volatility is not the same as a risk because volatility is merely the standard deviation of returns. Risk is the chance that an outcome or investment’s gains differ from an expected outcome or return.
Which Forex Pairs Move the Most?
The most volatile forex pairs by percentage in the last several years are USD/RUB, USD/TRY, USD/BRL, USD/ZAR, USD/SEK, and AUD/JPY. Forex pairs that move the most pips are USD/RUB, USD/TRY, and USD/ZAR. On the other hand, the least volatile currency pairs (primary) are AUD/NZD, EURCHF, EURUSD, AUDCHF, USDCHF, EURCAD, etc.
Please see the Table of the most volatile forex pairs in the last 52 weeks:
| Currency pair | Pips | % |
|---|---|---|
| USD/RUB | 23712.5 | 3.12 |
| USD/TRY | 3608.75 | 2.45 |
| USD/BRL | 821.17 | 1.75 |
| USD/ZAR | 2406.57 | 1.64 |
| USD/SEK | 1180.53 | 1.26 |
| AUD/JPY | 107.61 | 1.16 |
| NZD/JPY | 93.49 | 1.1 |
| USD/MXN | 2188.38 | 1.09 |
| NZD/USD | 71.55 | 1.05 |
| AUD/USD | 77.65 | 1.04 |
| CAD/JPY | 101.09 | 1.02 |
| EUR/AUD | 144.22 | 0.99 |
| AUD/CHF | 68.6 | 0.98 |
| EUR/NZD | 152.05 | 0.96 |
| GBP/JPY | 152.4 | 0.94 |
| EUR/JPY | 124.67 | 0.92 |
| USD/ILS | 294.75 | 0.91 |
| GBP/AUD | 150.12 | 0.86 |
| CAD/CHF | 62.91 | 0.85 |
| GBP/NZD | 160.91 | 0.84 |
| EUR/CAD | 111.53 | 0.82 |
| GBP/USD | 105.78 | 0.81 |
| USD/JPY | 98.72 | 0.8 |
| GBP/CHF | 97.09 | 0.8 |
| CHF/JPY | 104.4 | 0.79 |
| USD/DKK | 532.69 | 0.78 |
| EUR/USD | 85.51 | 0.78 |
| USD/CHF | 71.8 | 0.77 |
| AUD/CAD | 71 | 0.76 |
| GBP/CAD | 122.44 | 0.75 |
| USD/CAD | 93.59 | 0.74 |
| EUR/CHF | 68.97 | 0.67 |
| EUR/GBP | 55.7 | 0.67 |
| AUD/NZD | 69.25 | 0.64 |
| USD/SGD | 61.13 | 0.45 |
| USD/INR | 334 | 0.44 |
| USD/CNY | 205.46 | 0.32 |
| USD/HKD | 40.09 | 0.05 |
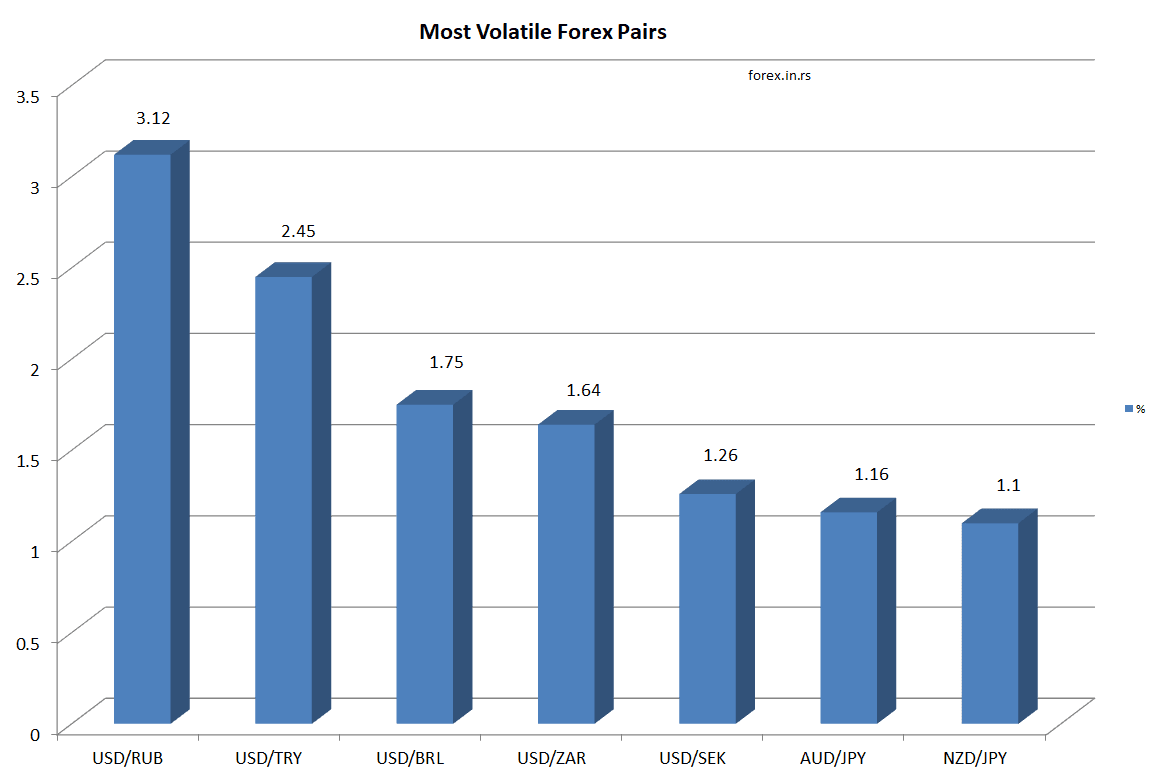
If we analyze percentage volatility moving in pips instead, we can see similar results. Exotic pairs and crosses pair with USD, and developing economies provide forex pairs that move the most pips (see Table below).
Table: Forex pairs that move the most pips
| Currency pair | Pips |
|---|---|
| USD/RUB | 23712.5 |
| USD/TRY | 3608.75 |
| USD/ZAR | 2406.57 |
| USD/MXN | 2188.38 |
| USD/SEK | 1180.53 |
| USD/BRL | 821.17 |
| USD/DKK | 532.69 |
| USD/INR | 334 |
| USD/ILS | 294.75 |
| USD/CNY | 205.46 |
| GBP/NZD | 160.91 |
| GBP/JPY | 152.4 |
| EUR/NZD | 152.05 |
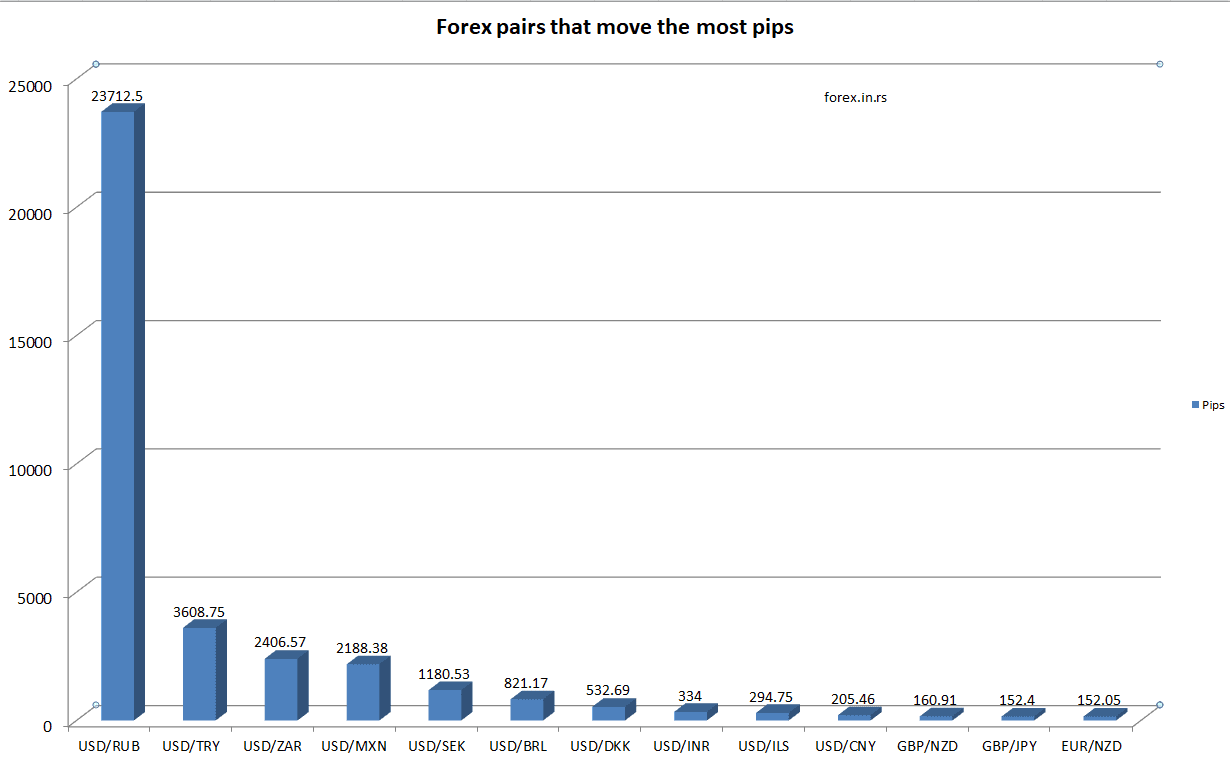
The Most Volatile Currency Pairs in 2022
The most volatile currency pair in 2022 was USD/RUB because of the Russian economy during the war. EU payments for Russian pipeline gas significantly impact the rising currency. Additionally, the most volatile currency pairs 2022 are USD/BRL, USD/ZAR, and USD/SEK (see Table below). The most minor volatile currency pairs are USD/HKD, USD/CNY, and USD/INR.
| Currency Pair | Pips | % |
|---|---|---|
| USD/RUB | 34145.8 | 4.49 |
| USD/BRL | 847.71 | 1.8 |
| USD/ZAR | 2454.41 | 1.67 |
| USD/SEK | 1394.16 | 1.48 |
| AUD/JPY | 122.91 | 1.33 |
| NZD/JPY | 103.44 | 1.22 |
| AUD/USD | 86.98 | 1.17 |
| CAD/JPY | 113.11 | 1.14 |
| NZD/USD | 77.79 | 1.14 |
| EUR/JPY | 149.77 | 1.1 |
| EUR/AUD | 158.89 | 1.09 |
| USD/MXN | 2183.24 | 1.09 |
| AUD/CHF | 75.27 | 1.08 |
| GBP/JPY | 174.85 | 1.08 |
| USD/ILS | 348.48 | 1.08 |
| EUR/NZD | 169.15 | 1.06 |
| USD/JPY | 120.7 | 0.97 |
| GBP/AUD | 164.94 | 0.94 |
| USD/DKK | 640.47 | 0.94 |
| GBP/NZD | 177.47 | 0.93 |
| EUR/USD | 99.13 | 0.91 |
| CHF/JPY | 119.38 | 0.9 |
| GBP/USD | 117.31 | 0.9 |
| CAD/CHF | 66.27 | 0.89 |
| EUR/CAD | 116.54 | 0.85 |
| GBP/CHF | 103.47 | 0.85 |
| USD/CHF | 79.3 | 0.85 |
| AUD/CAD | 77.65 | 0.83 |
| EUR/CHF | 80.77 | 0.79 |
| GBP/CAD | 128.74 | 0.79 |
| USD/CAD | 96.79 | 0.77 |
| EUR/GBP | 61.41 | 0.74 |
| AUD/NZD | 74.11 | 0.68 |
| USD/SGD | 66.15 | 0.49 |
| USD/INR | 346.45 | 0.46 |
| USD/CNY | 234.74 | 0.37 |
| USD/HKD | 36.55 | 0.05 |
Most volatile currency pairs in 2021
The most volatile forex pairs in 2021 based on variation are:
- AUDJPY (average volatility of 1.12%)
- AUDUSD (average volatility of 1.07%)
- EURAUD (average volatility of 1.07%)
- NZDJPY (average volatility of 1.05%)
- GBPAUD (average volatility of 1.05%)
- GBPNZD (average volatility of 1.05%)
As we can see, the most volatile currency pairs in the Asian session (significant pairs) are AUDJPY and AUDUSD based on price variation over the last five years. On the other hand, the most volatile currency pairs in the New York session are USDMXN, USDNOK, and EURNOK, while the most volatile currency pairs’ major forex pairs are GBPJPY and GBPUSD.
Who moves the forex market the least?
The least volatile currency pairs
Based on price variation, major currency pairs with low volatility are USD/CHN, EURCHF, EURUSD, AUDCHF, USDCHF, and EURCAD. Thus, the major currency pairs are generally less volatile than the emerging market ones.
While some currency pairs have a high correlation while others are comparatively less correlated, this correlation bifurcates primarily into positive and negative type Correlations. When a couple of currency pairs move side by side or in tandem, it is positively correlated, whereas a negative correlation occurs when the opposite happens. As a result, traders generally tend to avoid making any trade on more volatile currency pairs.
So, which forex pairs are generally the most moving?
Currency Pairs Types
Major, Minor, and Exotic Pairs are significant types of these currency pair types.
1. Major Pairs
The currency pairs that are the most traded globally are termed the major currency pairs. They are known for their colossal liquidity and lowest spreads. Listed below are some of them:
- USD/EUR (US Dollar/Euro)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar)
- CAD/USD (Canadian Dollar/US Dollar)
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar)
- USD/NZD(US Dollar/New Zealand Dollar)
One thing noticeable about these major pairs is that they have a US dollar occupying one of the sides because the US Dollar is undoubtedly the leading currency reserve globally, and about 88% of the forex trade happens in USD.
2. Minor Pairs
These currency pairs do not have USD on one of the sides. The three active minor currency crosses form the minor currency pairs, such as the yen, the Euro, and the UK GBP. Here’s the list:
- GBP/EUR (British Pound/Euro)
- EUR/CAD (Euro/Canadian Dollar)
- EUR/CHF (Euro/Swiss Franc)
- GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/CHF (British Pound/Swiss Franc)
- CAD/JPY (Canadian Dollar/Japanese Yen)
- CHF/JPY (Swiss Franc/Japanese Yen)
- GBP/AUD (British Pound/Australian Dollar)
- GBP/CAD (British Pound/Canadian Dollar)
3. Exotic Pairs
This pair comprises a more extensive and robust currency and a minor currency of a developing country. They generally have very high spreads. Here, we have listed some exotic pairs:
- EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish Lira)
- USD/NOK (US Dollar/Norwegian Krone)
- USD/SEK (US Dollar/Swedish Krona)
- USD/DKK (US Dollar/Danish Krone)
- USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand)
- AUD/MSN (Australian Dollar/Mexican Peso)
- USD/HKD (US Dollar/Hong Kong Dollar)
- NZD/SGD (New Zealand Dollar/Singapore Dollar)
Exotic currency pairs, such as USD/SEK, USD/BRL, and USD/DKK, are the most volatile and moving. Cross rates related to GBP, such as GBP/NZD, GBP/AUD, GBP/JPY, and GBP/CAD, are highly volatile currency pairs. On average, these cross-pairs move for more than 200 points (pips) per day.
Forex traders must be careful of deviations in any currency pairs and all other currency pairs and correlations for effective risk management. Positive or negative correlations of currency pairs give the traders an overview and a clear picture of the direction they should be trading and avoiding. In the forex trader’s best interest, focus on a currency pair with great potential and avoid choosing highly volatile ones. Since volatility is a crucial parameter that needs to be measured to understand market conditions, several ways of measuring volatility are listed below.
Volatility Measure
This helps in determining a current position. Listed below are the indicators that are used commonly:
1. Tue Average Ranges (ATR) – the best tool
Created by J.W. Wilder, this is widely used in measuring the price changes in currency. In addition, this is a widely used indicator in forex.
2. Moving Averages
The four major types of Moving Averages are:
- – Simple
- – Smoothened
- – Linearly Weighted and
- – Exponential MA
MA indicator helps us understand the market trend directions, whether they trend upward or downwards, and any possibility of reversals. They also help determine any flat market if the price neither increases nor decreases.
3. Donchian channels
This is one of the technical indicators that help measure relative volatility with other financial instruments. This indicator applies to almost all types of financial products, be it equities, futures, or currency markets, for that matter.
Thus, we have covered the three prescribed ways of measuring volatility. As a forex trader, you must know about volatility and ways to measure the currency’s price volatility.
Key factors that affect volatility
While trading in volatile currency pairs, technical aspects like resistance levels, support, and price patterns should be considered. Traders should remain updated with the latest Forex prices, supply, demand, political events, analysis, and news. They should be aware that any data released will affect volatility. Usually, technical analysis will be used by traders to measure volatility. Volatile currency pairs will show more price movement, which will be more frequent. Exotic currency pairs, including currency from emerging markets, will be more volatile since their economies are more unstable and the liquidity is also limited.
Many factors impact the market and affect its volatility. However, there are certain things that you must be aware of as a forex trader:
- Volatile currency pairs follow the technical areas for forex trading, like price patterns, resistance levels, support, etc.
- It would help if you stayed updated with all the latest forex news and price and analysis to analyze the market better. Any release of data can impact the volatility of currency pairs.
- Technical analysis helps traders with measuring volatility.
Apart from these factors, a forex trader must know what’s happening worldwide, such as massive news events like Brexit and trade wars that have enormous impacts on volatility.
Whenever a trader starts trading, he trades by speculating on a currency to get stronger or even weaker than the other, and if it achieves what the trader speculates or the goal, a profit is made. Now that you know the factors, let’s look at some significant types of currency pairs.
Research in South Africa indicates that more volatile currency pairs are usually more profitable since their prices fluctuate more rapidly. However, trading in the most fluctuating currency can also increase the risk. The factors affecting the foreign exchange (Forex) rate for all the currency pairs remain similar: geopolitics, the country’s economy issuing the currency, exports, imports, and differences in interest rates. In addition, extremely volatile currency pairs are usually less liquid than the more stable currency pairs. Hence, a well-planned strategy for risk management and trading is required.
List of most common traded forex pairs with high volatility
AUD (Australian dollar) /JPY(Japanese Yen): This currency pair is volatile since the AUD value is inversely related to the JPY. The AUD price is related to the value of Australian exports of metals, minerals, and other items, making it a commodity currency. The Japanese currency is preferred by investors when there are economic problems, making it a haven. So, the value of this currency pair fluctuates rapidly depending on the outlook for the world economy.
New Zealand Dollar(NZD)/ JPY(Japanese Yen): The value of the NZD is linked to New Zealand’s agricultural exports, making it a commodity currency like the AUD. Some of the major exports are honey, meat, eggs, and wood. Therefore, any change in the value of these commodities will affect the currency pair.
British pound(GBP) /Euro(EUR): Following Brexit, the pair’s volatility has increased. However, this could decrease in the future.
Canadian dollar(CAD)/ Japanese yen(JPY): The value of the CAD depends on the price of oil, making it a commodity currency, while the Japanese yen is a haven
British pound(GBP) /AUD(Australian dollar): Since Australia is a commonwealth member, the British and Australian economies are historically linked. Therefore, the price of the AUD is closely related to the Australian export value. There has been a decrease in Australian exports to China, increasing the volatility since the United States started its trade war with China.
US dollar(USD) /South African rand (ZAR): Gold is one of the major exports from South Africa and is priced in US dollars. This pair’s volatility depends on the gold price, with the exchange rate increasing with a gold price increase.
USD/South Korean Won(KRW): The KRW was formed after the second world war and traded at 1000:1 against the US dollar
USD/ Brazilian real(BRL): This currency pair value frequently fluctuates, making it popular among day traders and other traders with a scalping strategy
USD/Turkish Lira (TRY): The Turkish Lira has been highly volatile since the failed coup 2016. Significant changes in Turkish politics and society have resulted in fluctuations in currency value. Hence, traders are closely monitoring the currency pair due to the uncertainty involved.
USD/Mexican peso (MXN): The increase in disputes between the countries, and the change in tariff rate has increased the volatility
How trading strategy differs depending on volatility levels
The more volatile currencies will change their value over more pips than less volatile currencies. Hence, it is riskier to trade in highly volatile forex pairs. These highly volatile currencies are more likely to slip and make more significant moves, so selecting the position’s right size is more critical while trading. The major currency pairs are less volatile. These pairs are EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, and USD/JPY.
Trading considering forex volatility.
Traders who wish to trade in forex, taking advantage of the volatility, should take the following measures.
- find a suitable forex pair for trading
- analyze the fundamentals and technical aspects of the forex pair
- finalize a strategy for forex trading
- create a forex account for trading, depositing funds
- Open a position, monitor it, and close it
Volatile and stable currencies
The prices of different commodities are constantly changing. Volatility is often associated with fluctuation in prices. Forex traders consider volatility one of the most critical factors while opening or closing any trade. Financiers assess the risk involved by checking the volatility. They may reduce their transactions if the market is highly volatile since they will likely make more losses. Historical volatility is the standard deviation in the asset’s values, calculated using historical prices. Expected volatility is calculated using current prices and the expected risks.
Almost every currency can be volatile for some time. However, some currencies are more stable compared to others. These currencies usually represent economies with a low inflation rate, stable balance of payment, trade indicators, political system, balanced accounts for the government, predictable government monetary policy, and diversified economy with goods and services. Though volatility patterns are changing, financial experts consider a few currencies more stable than others. The currencies are Hong Kong, New Zealand, Singapore dollar, Norwegian Krone, and Swiss franc.
The governments in these countries maintain transparent government financial records and do not interfere in forex markets. As a result, the major currencies for forex trading, like the US dollar, Euro, British pound, Chinese renminbi, and Japanese yen, are also reasonably stable. In contrast, the currencies of some emerging market countries are highly volatile since they are affected by global demand and supply and local policy changes. These currencies are the Russian ruble, Brazilian real, Mexican, and Argentine peso.
Forex correlation pairs
Forex correlation represents the positive or negative relationship between two separate currency pairs. A positive correlation of 100% means that two pairs increase or decrease at the same level during the time. For example, EURUSD and USDCHF have a negative correlation because
Non-correlated forex pairs
Non-correlated currency pairs do not have positive or negative relationships, such as USD/CHF, USD/JPY, USD/CAD or NZD/USD, AUD/JPY, EUR/CAD, or GBP/CHF. For example, EURUSD and USDCHF are not non-correlated but negatively correlated. This is because non-correlated pairs do not have any relationship, and logically, these pairs are from different markets, such as EURCAD and AUDJPY.
Forex correlation and forex volatility are separate terms; there is no evidence that correlation increases or decreases volatility.
Conclusion
So, in the end, we can conclude that the forex market is total of irregularities. Hence, keeping a close eye on the market determinants and indicators that measure volatility is vital. Hence, a Forex Trader should be well-versed with Forex currency pairs and know what factors make currency pairs volatile and which Forex pairs move the most. That will ensure some certainty, stability, and, most importantly, peace of mind.
























