Table of Contents
When a person enters the financial markets, various parties are involved with the person, aka trader, deals. This includes banks, pension funds, insurance companies, institutional investors, and more. Therefore, you can expect to learn the following things from this article.
- Types of Financial Markets
- Participants of the Financial Market and how they are connected
- Financial Instruments
- Functions of Financial Markets
For a trader gaining the essential information for the market, they are trading in is necessary. For example, you must learn the alphabet from scratch to enter the forex market. You need to learn from your mistakes and experiences while applying your knowledge. You can also attend webinars and trade courses or watch articles on forex to gain more understanding.
If you are starting in this market, you need to have your hands on two forms of information: fundamental analysis and technical analysis. These would help him, in the long run, to sustain himself in the market. So, you might not need to learn about all the financial markets, but you need to know about the financial market you are dealing with!
Who are the participants in the financial markets?
The participants in the financial markets are commercial banks, corporations, governments, government-sponsored enterprises, futures market exchanges, money market mutual funds, brokers and dealers, and the Federal Reserve.
What is the financial market?
Financial markets represent a marketplace where traders trade assets such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, foreign exchange, and commodities. All the markets at national and international levels build the financial market.
What do you mean by the international financial market?
International financial markets represent monetary and macroeconomic interrelations between two or more countries. It consists of international banking services and the global money market.
What is the Institutional Structure of International Financial Markets?
The Institutional Structure of International Financial Markets comprises five key components: the foreign exchange market, credit market, insurance market, investment market, and stock market.
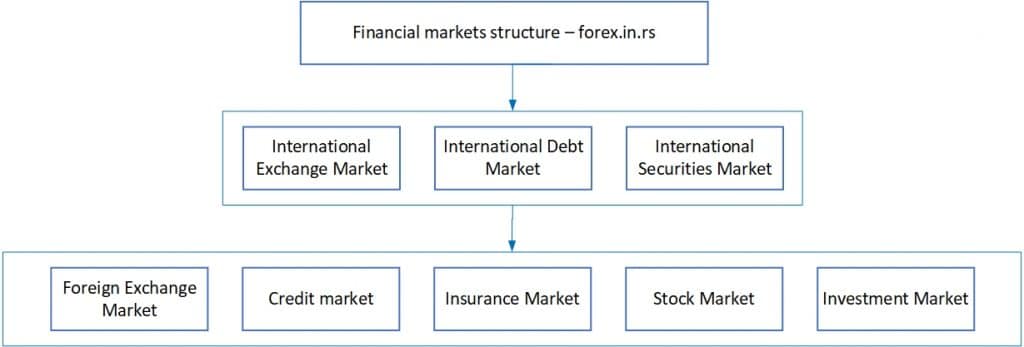
Structure of financial market diagram
There are three main parts of the world financial market, namely
- International Exchange Market
- International Debt Market
- International Securities Market
It is further divided into five segments, as below.
1. Foreign Exchange Market (Forex)
In this market, the asset traded is currency and its relevant equivalent. Many derivative instruments like CFDs are also get considered in this market. In the forex market, the settlement of trades can be in cash or non-cash, depending on the form, term of transactions, and market type. There are two types of markets here – Spot Market and Derivatives Currency Markets. For a derivatives market, a contract is
- Forward Contract: It is customized per the needs of two parties, and they agree to a specific rate. There is no guarantee here, and commercial banks are the intermediaries.
- Futures Contract: It is based on the current forex exchange rates. A guarantee is available, and the intermediary is always an exchange body.
- Options and Currency Swaps: All currency transactions can be done on the exchange or the over-the-counter market, depending on the trader.
2. Credit market
Simply put, the credit market redistributes extra funds from those who have them to those who don’t. However, it is complex compared to the investment market as it has a three-tier structure and requires higher requirements to fulfill its obligations.
Levels of Credit Market
- Central and Commercial Banks: In this prospect, the bank acts as a regulator. Through loans, the bank circulates the supply and demand of money, aids banks in trouble, and keeps them liquid to eliminate the cash gaps.
- Commercial Bank and Its Clients
- Legal Entities and their Credit Relations
3. Insurance Market
From the global stance, insurance companies have a firm hold on the market, being the most prominent investors, and thus they have a different market. They give different kinds of services for which they get funds, and they park these funds in the financial markets, metals, etc., too opposed to the inflation cost and maintain profitability.
4. Investment Market
The investment market is free competition and a partnership-based concept between various agents in the investment market. It is similar to the stock market as it involves dealing with funds parked insecurities, but unlike the stock market, it also deals with fixed assets, capital investments, and more. In short, the investment market involves dealing with all financial assets to take advantage of price hikes and dividend payouts.
5. Stock Market
The stock market is a relationship between the market participants and the securities. Securities here can be traded on exchanges as well as over the counter. Though to trade securities on an exchange, it has to be listed. There are various types of securities in the stock market, which include,
- Stocks: These are common stocks or preferred stocks. The difference is that the common stockholders have the right to vote, whereas the preference shareholders may not have it. Though preference shareholders enjoy a fixed dividend, it is conditional on profitability and company decisions.
- Bonds: There are various types of bonds, as stated below.
Company Bonds – Issued by Company
Municipal Bonds – Issued by the Local Authorities
State / International Bonds – For example, Eurobonds
Bonds also prefer people to have an average of getting the money back if a company defaults or decides to liquidate. For bondholders, two things are significant – Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity.
- Indices: Indices are a basket of various securities that shows the average rate stats for a specific sector or industry. For example, Auto Indices may have all the significant stocks of auto sector firms and shows the average share rate.
- Derivatives: It is a very complex derived instrument, mainly used for hedging.
- ETF Securities: ETF or Exchange Traded Funds are index funds whose units are traded on an exchange. The funds can be anything from a company’s stock to a portfolio having gold and metals. So it gives more options for trades.
The currency market accounts for 1/5 share of the financial market. Therefore, apart from the classification stated above, one can also classify the financial market in a broader sense into three categories – the Currency Market, the Stock Market, and the Commodity Market.
The currency market has all the world currencies, including the new-age cryptocurrency. The stock market has all the items related to securities, and the last commodity market includes oil, metals, goods, services, and rare investments like art, antiques, etc. These markets are interconnected.
What are the functions of the financial market?
The financial market’s motive is to mobilize capital, distribute it, control and maintain its reproduction, and increase an economic cycle and system’s overall efficiency. Here is the list of functions that market participants play in the financial market.
But why do financial markets matter?
The functions of international financial markets are:
- Monitor and regulate the financial system process by overlooking compliance control, maintaining money supply, legal supervision, etc.
- Maintains and provides different relationships between the market players, including individual investors, institutional investors, private investors, etc.
- It allocates the capital in a way that can increase efficiency and create more value.
- Reduces the risk, prevents fraud, including money laundering, maintains transparency, and tries to erode rate manipulation in the market.
- Creates and maintains liquidity in the market.
- Keeps transactions secured and transparent.
- Provides essential information and data.
The international financial market is a complex system of interconnected markets and institutions that facilitate the flow of payments between countries, individuals, and businesses. It is an essential component of the world’s economic infrastructure and an important source of capital for global economic development. The functions of this global financial market are necessary to ensure a healthy and prosperous global economy.
First and foremost, the international financial market facilitates cross-border payments. This way, it connects entities from different countries with different currencies and enables them to transact. This function is especially vital for developing countries that may not have access to traditional banking services or advanced payment systems. The international financial market also encourages foreign direct investment into these more vulnerable economies by providing access to international payments.
Another significant role played by the international financial market is in risk management. It reduces overall portfolio risk through diversification by allowing investors to spread their investment portfolios across different assets, currencies, needs, and regions. Furthermore, it will enable investors to take advantage of hedging strategies such as futures contracts or options contracts which can protect from currency fluctuations or other changes in the value of investments.
The international financial market also plays an essential role in providing liquidity for the global economy. Allowing investors to convert their investments into cash quickly when necessary can provide much-needed liquidity during economic volatility or stress. This liquidity makes it possible for corporations to meet short-term obligations and invest in long-term initiatives when opportunities arise. The availability of liquidity can also help governments manage their fiscal policies more effectively by enabling them to respond more quickly when necessary.
Finally, the international financial market promotes price transparency and efficiency within the global economy. By providing a platform where buyers and sellers can publicly post bids and ask prices on various products and services traded around the world, it helps create a level playing field where all participants have access to information that allows them to make informed decisions about where they should allocate their resources most efficiently. Similarly, by creating competition between buyers and sellers within each asset class or region, it helps keep prices fair and efficient so that everyone benefits from equitable transactions across borders without artificial advantages or disadvantages based on location or nationality.
In conclusion, the functions performed by the international financial market are essential for driving global economic growth while helping investors mitigate risk while maximizing returns on their investments over time. Without this crucial mechanism connecting nations through cross-border payments while facilitating risk management strategies and price discovery mechanisms within an efficient marketplace full of opportunities for all participants alike – there would be no true globalization possible as we know it today without its presence in our lives!
In simple words, the seven main functions of financial markets are:
- Price Determination.
- Funds Mobilization.
- Liquidity.
- Risk sharing.
- Easy Access.
- Reduction in Transaction Costs and Provision of the Information.
- Capital Formation
Financial markets lean on central banks to control the currency rates as they decide interest rates. Simultaneously, the stock and the currency market directly correlate with the traded financial asset’s progress and changes. The most exciting market for traders remains the security market, which requires fewer funds and has extraordinary volatility.
Participants of the Financial Market
The answer to this is simple; all of us are market participants. We work at a place or do a job, contributing to GDP (Gross Domestic Product). We buy or sell things associated with the Consumer Price Index (CPI), aka inflation rate. Many people also invest or trade in forex, park their money in the banks, take loans, or land money. All of these things are financial activities.
Though in a precise way, financial market participants are classified based on the segment. In layman’s language, financial markets are nothing but relationships between the buyers and the sellers. It also has another category known as intermediaries that look after transactions, assist, and provide necessary facilitation. Through this, the intermediary can simultaneously act as a buyer, seller, and intermediary.
We have classified the players of financial markets for each market. So, let’s dive into it.
1. Forex Market
- Buyers: All sellers, agents, etc., may also perform the role of buyers.
- Sellers: Mostly, all the significant sellers and banks or state bodies. A state must perform a regulatory function if it sells currencies through an authorized body. So a lot of sellers are also large companies here.
- Intermediaries: Here, primarily commercial players are involved.
2. Credit Market
- Borrowers: Borrowers in this market are on two segments – international level and national level. At the international level, the borrowers are known as states, and here the debt-to-GDP ratio is considered the leading indicator. Companies, individuals, and local governments are the borrowers at the national level. One example is the U.S. mortgage system, in which banks issue various securities to lend more and secure new capital.
- Lenders: Here, market players have extra capital, aiming to create more. These individuals are people or companies that park their wealth in investment funds, pension funds, etc. They give money and thus are called lenders; they benefit from interest income or dividends. States are also said to be lenders to enhance liquidity and distribute it using the central bank.
- Intermediaries: The intermediaries are the organizations that look after capital distribution, like banks, dealers, brokers, and investment management companies. We can also add insurance and pension companies here as they also gather and distribute money. The credit market can be like investment or the stock markets; for example, it helps raise capital and security when discussing corporate bonds. Generally, government bonds are a popular option compared to investment funds as they have low risk.
3. Insurance Market
- Insurers: Insurers are the companies that provide insurance services. There are three types of insurance providers – Open type, which provides insurance to all the market participants, Captive Insurers (their insureds control them, and lastly comes reinsurance risk management companies.
- Insureds: Individuals, institutions, or companies that buy insurance products reduce the overall risks.
- Intermediaries: The good thing about this market is that there are no intermediaries, as all the transactions occur between the insurer and the insured.
As markets are interconnected, in this case, insurance companies are involved in the investment market too. Insurance instruments like swaps, futures, etc., are traded on the stock market.
4. Investment Market
The investment market includes all the people who invest their money in a financial asset as an investor. In this market, banks, exchanges, etc., act as intermediaries.
5. Stock Market
The following are the market participants in the stock market.
- Security Issuers: This category includes firms, companies, etc., who issue securities like bonds, stock, and more. They have to abide by the rules to issue securities when giving it.
- Investors are those who purchase securities to increase or create income. There are two types of investors – Strategic ones, who buy a majority in a company’s stock, and minorities, who buy securities to develop revenues and build a portfolio.
- Intermediaries: Here, stock exchanges, underwriters, banks, auditors, rating agencies, etc., act as intermediaries. They help in issuing and placing securities in the market.
We can also classify all these categories in a group, as stated below.
- The Central and State Banks: This includes regulatory organizations as well. They manage the capital and overlook the performance and regulatory requirements.
- Regulators: The participants do not perform transactions but have a controlling duty over them. A state or central bank can also plate the same part, government, or a separate organization for that, i.e., a Self-regulatory Organization (SRO).
- Financial Service Companies: These companies give financial services and act as an intermediary. They look after various aspects, including stocks, forex, commodity exchanges, brokers, auditors, underwriters, registrars, clearinghouses, consulting firms, etc.
- Banks: They act as financial intermediaries. They look after cash distribution and regulate and supervise the market to abide by the regulatory authorities’ compliance.
- Legal Entities: These include borrowers, investors, lenders, etc. Also, companies involved in parking or investing clients’ funds in various funds like pension schemes, insurance, hedge funds, trust management firms, brokers, individual organizations, dealers, etc., are called legal entities.
- Individuals: Individuals also include borrowers, investors, and lenders. From a broader perspective, these people are traders, speculators, long-term investors, asset managers, or ordinary people.
Market Indicators
Just having the essential information is not enough for a trader; there is a lot more to it, and one such thing is market indicators. The indicators here include micro and macroeconomic data, forecasts, analysis, and much more, which get released from time to time. For example, the unemployment rate, GDP, inflation rate, securities growth, currency rates, etc., act as indicators.
Read more in our article, Key economic indicators.
That’s why most traders consider economic indicators an essential part of their trading. So if you are still not clear about the indicators and their impacts, worry not, as we have covered you.
1. Interest Rate
The interest rate can be the most significant economic indicator as it helps manage the money supply and helps in adjusting the inflation rate. At this rate, the loans are given to commercial banks by the central bank. Therefore, a high rate increases the rates of deposits and credits and motivates customers to invest more. This also reduces the rate of inflation.
There are broader benefits of this rate increase as well. For example, in an advanced economy like the U.S., if the Federal Reserve hikes the rates, it boosts the dollar’s value. Thus, this move also helps reduce the stagnation and interest of more investors.
2. Non-farm Payrolls
Non-farm Payrolls suggest a change in the total number of employees in the non-farm sectors of the U.S. Therefore, it is critical data and impacts the dollar rate highly. It gets released on the first Friday of every month around 1:30 pm GMT.
If the actual data deviates more than 40,000 compared to the expectations, it affects the U.S. dollar exchange price. In reality, it depends on the data and how investors react.
3. Consumer Price Index (CPI)
CPI is a stat that shows a change in the price of consumer goods and services being bought by a nation’s households. It shows the difference in the cost of living due to changes in the price of goods and services. It is compared to the benchmark indicator for knowing the performance.
Generally, this base is referred to by EBRD, IMF, UN, etc. There are various calculation methods, like Paasche, Lowe Index, or Laspeyres Price Index. The decline in this index suggests lower consumer purchasing power and higher inflation growth.
If the indicators are positive, investors will react strongly to that, eventually impacting the financial markets. Remember that along with all these; you should also keep yourself aware of the economic calendar.
It lists all the main economic events worldwide, and you should form your strategies around them to avoid repercussions. When the news gets released, it increases the volatility; thus, knowing it in advance can help you enter and exit the market on time.
Tips for Trading on Economic Indicators
Here are a few tips that would help you out if you want to trade around economic events.
You should compare the released data with the forecasted data. For example, if the U.S. GDP is predicted to be 3%, but it came out to only 2.4%, it is negative news. But be aware of the fact that the data can also be revised.
Evaluate your expectations and reality. Often, the news is already traded, and thus no significant impact is seen when releasing the news. I.e., when the Fed is likely to increase the interest rate in the forthcoming meetings, investors would already be suspecting and trading accordingly. So, when the Fed finally raises the rates, there will be less volatility than expected.
Be observant and keep yourself updated with other factors as well. Sometimes significant events overshadow essential data releases and have no impact on the market. For example, during the U.S.- China trade war, the U.S. crude oil stockpile data was released, which generally affected the exchange rates and other financial assets. But due to the trade tensions, it went unnoticed.
Conclusion
We hope we have helped you understand the institutional structure of international financial markets. There are many layers you have to pill to get to the depth of this realm.
You can do wonders in this field while enjoying it with consistency and hard work. So, brace yourself, keep yourself updated, and learn from your mistakes. Hasta La Vista, until the next time!
























