Table of Contents
In the intricate dance of the stock market, the stability and growth of share prices are influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from economic indicators to company performance metrics. However, one of the most dramatic and immediate impacts on a company’s stock can arise from the revelation of a scandal. When a scandal hits a major corporation, it sends shockwaves through the market, affecting the company’s share price and the broader financial landscape.
In past articles, we analyze forex rigging scandals and various forex scams, including forex signals scams. We know that forex as a business is not a scam, and forex is not rigged. Businesses can be legitimate, but some people can be greedy or unethical, leading to big corporate scandals.
This article delves into the complex relationship between corporate scandals and share price volatility. It explores how these events can undermine investor confidence, trigger regulatory responses, and lead to significant financial repercussions for the involved entities and their stakeholders. By examining historical examples and analyzing how scandals affect the market, we will shed light on the importance of corporate governance, transparency, and ethical business practices in maintaining shareholder trust and market stability.

A big corporate scandal involves significant revelations about a company’s involvement in unethical practices, fraud, or misconduct that severely damages its reputation and stakeholder trust. These scandals often come to light through evidence of financial manipulation, misleading accounting methods, engaging in unethical or illegal business activities, or failure to protect sensitive data.
You can check my video about company scandals:
Additionally, actions that result in environmental harm or negligence towards regulatory compliance can also trigger a corporate scandal. Such events tarnish the company’s public image. They can lead to legal consequences, financial losses, and a significant drop in share prices, reflecting the market’s reaction to the erosion of ethical standards and trust.
This is a list of the 15 biggest corporate scandals:
- Enron (2001): Enron’s collapse due to accounting fraud marked one of the most significant bankruptcy filings, leading to significant changes in U.S. financial regulation.
- WorldCom (2002): The telecommunications giant filed for bankruptcy after revealing $11 billion in accounting fraud, one of the most significant instances of corporate fraud ever.
- Lehman Brothers (2008): The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers significantly contributed to the global financial crisis, highlighting the dangers of risky investment strategies in the subprime mortgage market.
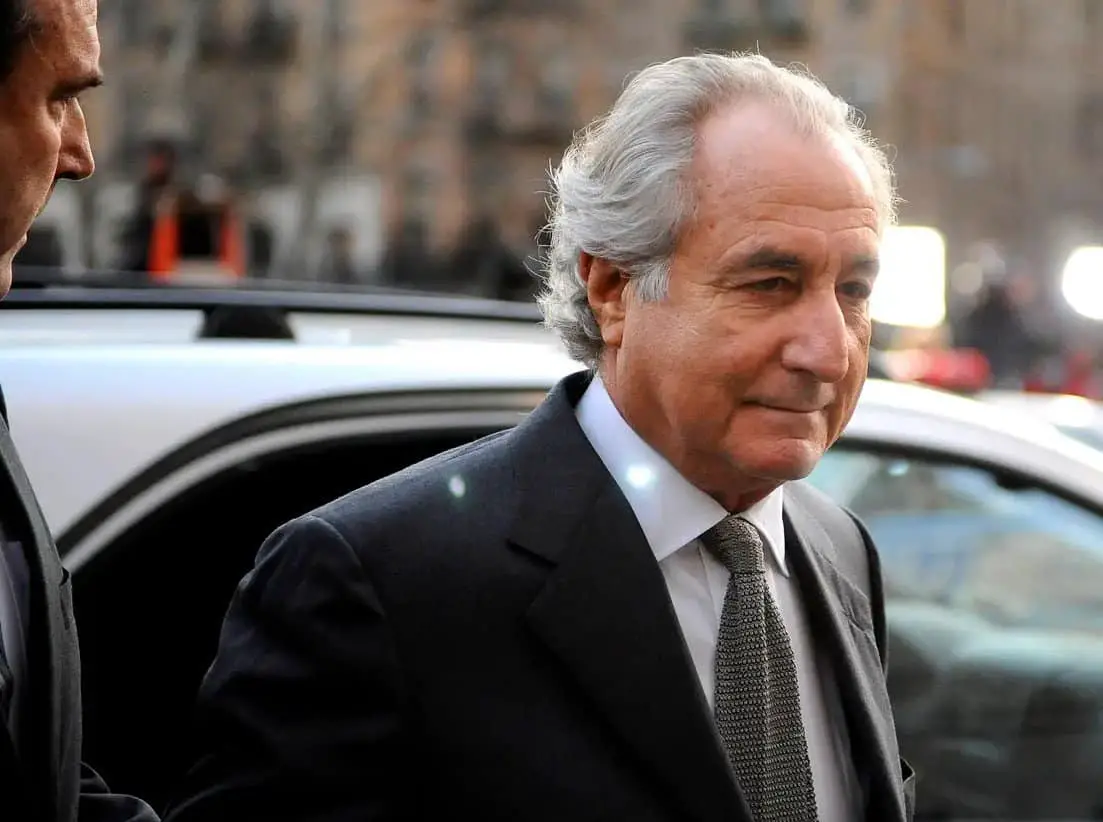
- Bernard Madoff Investment Scandal (2008): Madoff’s Ponzi scheme, the largest in history, defrauded investors of billions of dollars, revealing severe lapses in financial oversight.
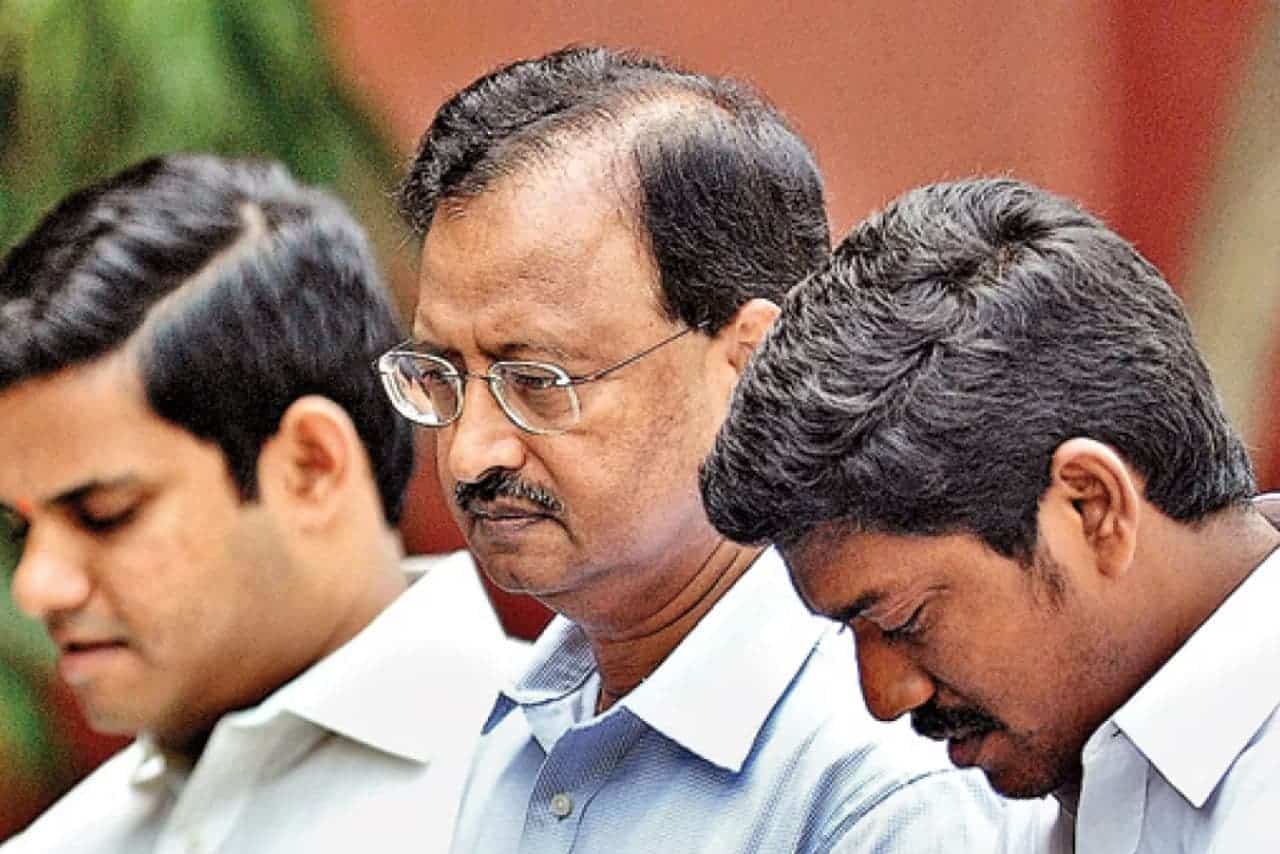
- Satyam Scandal (2009): India’s Satyam Computer Services admitted to falsifying accounts by $1.47 billion, becoming one of the country’s most significant corporate frauds.
- BP Oil Spill (2010): The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, one of the worst environmental disasters in U.S. history, was caused by a blowout at a BP-operated oil well.
- Siemens Bribery Scandal (2008): Siemens was found to have engaged in widespread global bribery to secure contracts, resulting in $1.6 billion in fines and a comprehensive overhaul of its corporate governance.
- Apple (2012): Allegations of labor abuses and poor working conditions in Apple’s supply chain, particularly concerning its Chinese factory workers, drew global attention.
- Valeant Pharmaceuticals (2015): Valeant was criticized for price gouging and accounting irregularities, leading to investigations and a significant stock price decline.
- Volkswagen Emissions Scandal (2015): The revelation that Volkswagen rigged emissions tests for millions of its diesel vehicles led to billions in fines and a global scandal.
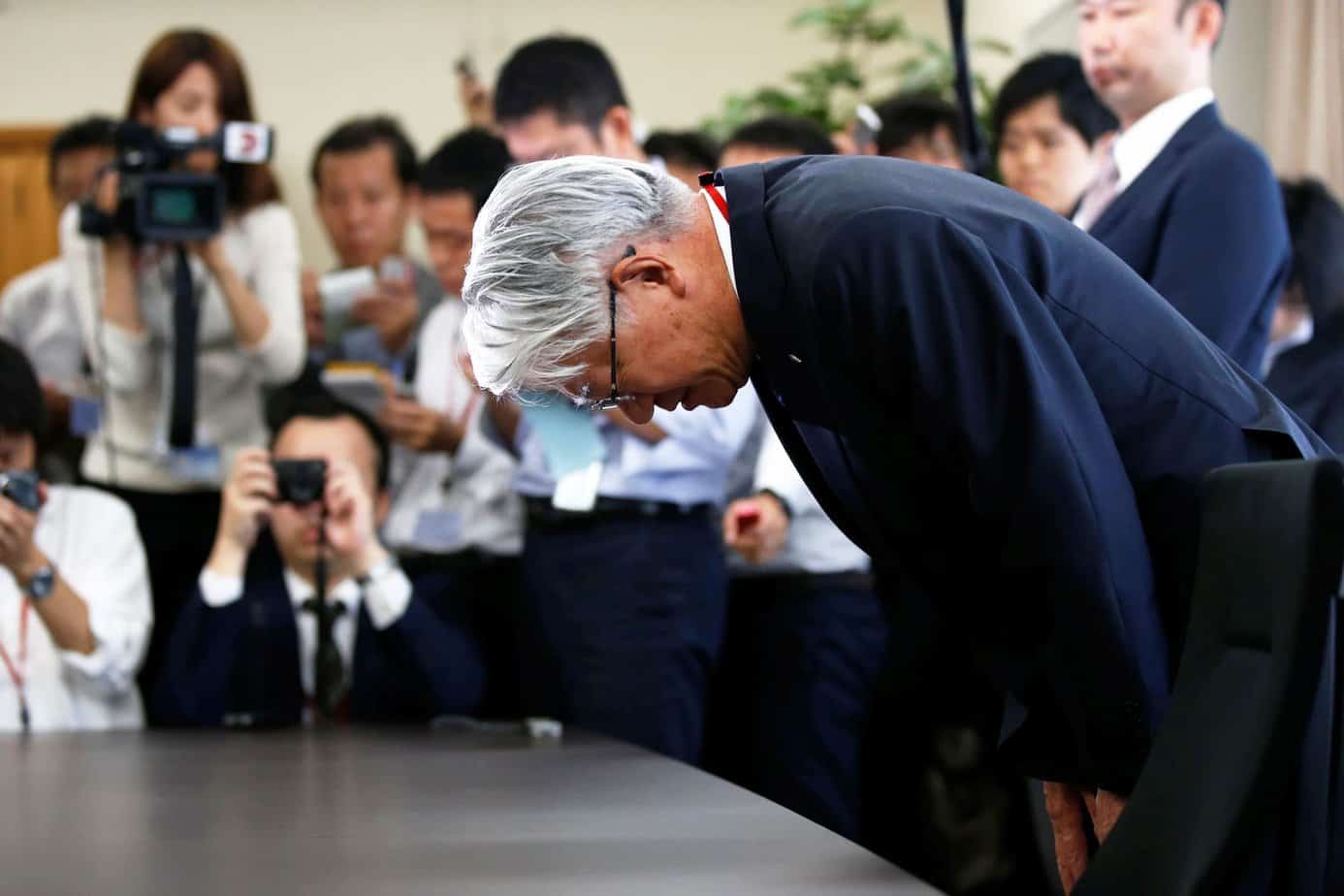
- Kobe Steel (2017): Kobe Steel admitted to fabricating data on the quality of its aluminum and copper products, affecting hundreds of companies and numerous industries.
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): A massive data breach at Equifax exposed the personal information of 147 million people, raising severe data security and privacy concerns.
- Uber (2017): Uber faced a series of scandals, including issues related to sexual harassment, data privacy, and unethical business practices, significantly damaging its reputation.
- Facebook (Cambridge Analytica, 2018): The misuse of Facebook user data by Cambridge Analytica to influence elections sparked a significant controversy over privacy and data protection.
- Theranos (2018): Theranos, led by Elizabeth Holmes, was accused of fraudulently claiming to have revolutionized blood testing, leading to the company’s collapse and legal battles.
Enron Big Corporate Scandal (2001)
The Enron scandal, surfacing in 2001, remains one of the most infamous corporate fraud cases in history, illustrating the depths of corporate malfeasance and leading to sweeping reforms in financial regulation. Once a titan in the energy sector, Enron Corporation engaged in an elaborate accounting fraud that concealed its financial woes and inflated its profitability, misleading investors, employees, and the public about its proper financial health.
Background
Founded in 1985 by Kenneth Lay, Enron grew from a natural gas pipeline company into a significant energy, commodities, and services company. By the late 1990s, Enron was hailed as a new business model, lauded for its innovation and seemingly robust financial performance. It was the largest natural gas and electricity marketer in the United States, with reported revenues of $101 billion in 2000.

The Enron Scandal
The crux of the Enron scandal was the use of complex accounting loopholes and special purpose vehicles (SPVs) or particular purpose entities (SPEs), which allowed the company to hide billions of dollars in debt from failed deals and projects. These techniques were facilitated by a network of partnerships to keep financing off Enron’s balance sheet, thus inflating its stock price and hiding its liabilities.
The company’s accounting was complicated by “mark-to-market” accounting. This method allowed Enron to book potential future profits on the day a deal was signed, regardless of the profits that might ultimately be realized. This practice led to vast overstatements of value.
Enron Collapse
Enron’s financial instability was eventually revealed, leading to a crisis of confidence among investors. Its stock price peaked at $90 per share in mid-2000 and plummeted to less than $1 by the end of November 2001. On December 2, 2001, Enron filed for bankruptcy, the largest in U.S. history.
Enron Aftermath
The Enron scandal had far-reaching consequences. Thousands of employees lost their jobs, and investors lost billions of dollars. The fallout also led to the dissolution of Arthur Andersen, one of the world’s five largest audit and accountancy partnerships, for its role in obstructing justice and its failure to protect the public interest as Enron’s auditor.
Enron Regulatory Response
In response to the scandal, the U.S. Congress passed the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX), aimed at protecting investors from the possibility of fraudulent accounting activities by corporations. The SOX Act imposed stricter regulations on accounting practices, increased penalties for financial fraud, and required greater transparency in financial reporting by corporations.
Enron Legacy
The Enron scandal remains a cautionary tale of how greed, hubris, and a culture of unethical behavior can lead to disaster. It serves as a benchmark for discussions on corporate ethics, governance, and the importance of oversight in financial reporting. The scandal reshaped how businesses are regulated and audited in the United States, highlighting the critical need for transparency, integrity, and accountability in corporate governance.
WorldCom, once the second-largest telecommunications company in the United States, experienced rapid growth through acquisitions in the 1990s. Founded in 1983 by Bernard Ebbers, WorldCom transitioned from a small long-distance telephone service provider to a global telecommunications powerhouse. Its aggressive expansion strategy was primarily financed through debt, and the company became a symbol of the dot-com era’s excesses.
WorldCom Big Corporate Scandal (2002)
The core of the WorldCom scandal was the improper accounting of approximately $11 billion in expenses. WorldCom’s management, under CEO Bernard Ebbers, began classifying operating expenses as capital expenditures to maintain its stock price and meet Wall Street expectations. This manipulation allowed WorldCom to inflate its assets and profitability artificially, misleading investors and analysts about its financial condition.
Additionally, WorldCom exaggerated revenue through various accounting tricks, including creating bogus accounting entries and transferring costs to capital accounts. These practices were designed to hide the company’s deteriorating financial health caused by the bursting of the dot-com bubble and the intense competition in the telecommunications sector.

WorldCom Collapse
The unraveling of WorldCom began in June 2002 when the company disclosed that it had improperly accounted for more than $3.8 billion in expenses. This revelation was the first in a series of disclosures that eventually totaled around $11 billion in fraudulent accounting, making it one of the largest accounting scandals in history. The scandal led to a significant loss of investor confidence, and WorldCom’s share price plummeted. On July 21, 2002, unable to secure additional financing and facing mounting debts, WorldCom filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. At the time, it was the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history.
WorldCom Aftermath
The WorldCom scandal devastated employees, shareholders, and the telecommunications industry. Approximately 30,000 employees lost their jobs, and shareholders lost billions of dollars as WorldCom’s stock became worthless. The scandal also contributed to a significant loss of trust in corporate America after the Enron scandal.
Bernard Ebbers was found guilty of fraud, conspiracy, and filing false documents with regulators. He was sentenced to 25 years in prison, although he was released early in December 2019 due to health issues and died in February 2020.
WorldCom Regulatory Response
The WorldCom scandal, along with Enron and other corporate frauds, prompted significant changes in regulation and governance. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 enhanced corporate governance and financial disclosure to prevent similar scandals. The act introduced stringent rules for corporate accountability, including stricter audit regulations and penalties for fraudulent financial activity.
WorldCom Legacy
The WorldCom scandal remains one of the most significant instances of corporate fraud in history. It serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of unethical management and the importance of transparency and integrity in corporate governance. The scandal also highlighted the need for stronger regulatory oversight and reforms in accounting practices, contributing to a more cautious and regulated corporate environment in the years following the scandal.
Lehman Brothers Big Corporate Scandal (2008)
BP Oil Spill Big Corporate Scandal (2009)
The BP Oil Spill, also known as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, unfolded on April 20, 2010, in the Gulf of Mexico and is recorded as one of the worst environmental disasters in U.S. history. The incident involved the offshore drilling rig Deepwater Horizon, leased by the oil giant BP (British Petroleum). The rig was situated approximately 41 miles off the coast of Louisiana, drilling an exploratory well at a depth of about 5,000 feet in the Macondo Prospect.
The Catastrophe
The disaster began with a blowout, a sudden release of crude oil from the well under high pressure, which ignited and resulted in a massive explosion on the rig. The explosion claimed the lives of 11 workers and injured several others. Following the initial blowout, the rig eventually sank two days later, leaving the healthy gushing oil into the Gulf at an alarming rate.

Efforts to cap the well and contain the spill were met with numerous challenges, leading to the release of millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf over 87 days. It was not until July 15, 2010, that the oil flow was successfully halted, and the well was permanently sealed on September 19, 2010.
Environmental Impact
The environmental consequences of the spill were catastrophic. The released oil covered thousands of square miles of ocean surface, affecting marine life, contaminating the shores of the Gulf states, and disrupting ecosystems. The spill caused extensive damage to marine and wildlife habitats, killed thousands of marine animals and birds, and significantly impacted the region’s fishing and tourism industries.
Aftermath and Response
In the wake of the spill, BP faced intense scrutiny and criticism for its role in the disaster and its handling of the response efforts. The company committed billions of dollars to the cleanup operation, compensation for economic losses, and restoration projects in the affected Gulf states. Several investigations were launched to determine the causes of the disaster, leading to findings that highlighted failures in risk management and safety procedures on the part of BP and its partners.
Regulatory and Industry Changes
The BP oil spill prompted a reevaluation of offshore drilling practices, leading to tighter regulations and safety standards in the industry. The U.S. government imposed moratoriums on new deepwater drilling permits and introduced new rules to strengthen oversight of offshore drilling operations. The industry began to focus more on risk management, emergency response, and safety culture to prevent future disasters of similar magnitude.
Legacy
The legacy of the BP oil spill is multifaceted. It is a sad reminder of the environmental risks associated with oil exploration and production, especially in deepwater settings. The disaster spurred ongoing scientific research into the environmental impacts of oil spills and the development of more effective oil spill response technologies. It also increased public awareness and debate over the reliance on fossil fuels and the need for sustainable energy sources. The BP oil spill remains a case study in environmental science, crisis management, and corporate responsibility, highlighting the critical importance of balancing energy development with environmental protection and safety.
Siemens Bribery Big Corporate Scandal (2008)
Siemens AG, a multinational conglomerate headquartered in Munich, Germany, and one of the world’s largest producers of energy-efficient technologies and electronics, faced a scandal of unprecedented scale in 2008. The company, dating back to 1847, was embroiled in a global corruption scandal that revealed systematic bribery and corrupt practices to secure contracts in various countries worldwide.
The Siemens AG Scandal
The Siemens bribery scandal came to light following investigations by the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) and the German authorities. It was uncovered that Siemens had been engaging in corrupt practices for many years, using slush funds to bribe government officials, secure public contracts, and gain illicit market advantages globally. The investigations revealed that Siemens had paid an estimated $1.4 billion in bribes in numerous countries, including Argentina, Israel, Venezuela, China, Nigeria, and Russia.

Bribery practices were deeply ingrained in Siemens’ corporate culture, and the company employed elaborate systems to conceal its activities. These included using off-book accounts, sham consulting contracts, and other sophisticated means to facilitate and disguise its corrupt payments.
Siemens AG Legal and Regulatory Response
The revelations about Siemens’ practices led to one of the largest and most significant enforcement actions under the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) and similar anti-corruption laws in other jurisdictions. In 2008, Siemens agreed to a landmark settlement with the DOJ, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and German authorities. The company consented to pay fines and penalties totaling approximately $1.6 billion, one of the most significant corruption penalties ever imposed.
As part of the settlement, Siemens also agreed to implement extensive changes to its corporate governance, compliance procedures, and business practices. This included appointing an independent compliance monitor to oversee the company’s reform efforts and ensure adherence to international anti-corruption standards.
Siemens AG Corporate Governance Overhaul
The scandal prompted Siemens to overhaul its corporate governance and compliance systems comprehensively. The company initiated sweeping reforms designed to prevent future instances of corruption. These measures included establishing a more robust compliance and control system, extensive anti-corruption training for its employees, and creating a new, centralized compliance division. Siemens’ efforts to reform its corporate culture and practices became a case study of how a global corporation can recover from widespread corruption.
Siemens AG Legacy and Lessons Learned
The Siemens bribery scandal had far-reaching implications for the global business community. It underscored the importance of ethical business practices and the need for stringent compliance with anti-corruption laws worldwide. The scandal also highlighted the risks associated with inadequate oversight of corporate conduct and the potential consequences of failing to maintain ethical standards in business operations.
In the years following the scandal, Siemens emerged as a corporate compliance and ethics leader, sharing its experiences and lessons learned with the broader business community. Despite significant ethical and legal challenges, the company’s recovery and transformation illustrated the potential for positive change. The Siemens case remains a pivotal example of the impact of global corruption and the vital role of compliance and ethics in modern corporate governance.
Uber Big Corporate Scandal (2017)
In 2017, Uber, the global ride-hailing giant, encountered a tumultuous period marked by a series of scandals that significantly impacted its reputation and operational framework. These controversies spanned a range of issues, including corporate culture problems, allegations of sexual harassment, data privacy breaches, and unethical business practices. These incidents prompted widespread criticism from the public, regulators, and Uber’s stakeholders.

Sexual Harassment and Uber Corporate Culture Issues
One of the most striking revelations came in February when a blog post by a former Uber engineer detailed systemic issues of sexual harassment, discrimination, and a toxic work environment. The post sparked an investigation led by former U.S. Attorney General Eric Holder, culminating in a comprehensive report with recommendations for change. The investigation revealed a workplace culture that was permissive of inappropriate behavior, lacked sufficient mechanisms for addressing employee complaints, and prioritized growth over ethical concerns.
Uber Data Privacy and Security Breaches
Uber also faced significant scrutiny for its handling of user data and privacy. The company disclosed a breach in 2016 that affected 57 million Uber users and drivers, revealing that it had concealed the hack for over a year. Uber paid a $100,000 ransom to the attackers in exchange for deleting the data and keeping the breach secret, a decision that drew criticism for its lack of transparency and accountability.
Uber’s Unethical Business Practices
The company was accused of employing aggressive and unethical tactics to expand its market share and undermine competitors. This included using software tools like “Greyball” to evade law enforcement in cities without authorized service. Additionally, Uber faced legal challenges and regulatory pushback across various markets due to its disregard for local taxi laws and labor regulations concerning driver classification.
Uber Leadership and Organizational Changes
The accumulation of these scandals led to significant leadership changes at Uber. Co-founder and CEO Travis Kalanick resigned in June 2017 amid pressure from investors concerned about the company’s direction and ethical standing. His departure marked a turning point for Uber, which then embarked on a mission to overhaul its corporate culture, improve its public image, and stabilize its operations under new leadership.
Uber Reform and Reputation Management
In the aftermath of the 2017 scandals, Uber committed to implementing the recommendations from the Holder report, which included measures to strengthen its corporate governance, enhance transparency, and build a more inclusive and respectful work environment. The company also improved its data security practices and rebuilt trust with its users, drivers, and regulators.
Uber Legacy
The events of 2017 served as a critical lesson for Uber and the broader tech industry on the importance of ethical business practices, corporate responsibility, and the need to balance innovation with respect for laws and societal norms. Uber’s journey through these scandals underscored the challenges of managing rapid growth while maintaining a commitment to ethical principles and corporate accountability. The company’s efforts to address these issues and reform its practices reflect an ongoing process of transformation and adaptation in pursuit of sustainable success.
Facebook Cambridge Analytica Big Corporate Scandal (2018)
In early 2018, Facebook became embroiled in a major controversy involving Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm known for its data-driven campaign strategies. This scandal highlighted significant issues regarding privacy, data protection, and the ethical use of personal information in the digital age. It was revealed that Cambridge Analytica had improperly accessed the data of millions of Facebook users without their consent and used this information to target political advertising and influence voter behavior in various elections worldwide, including the 2016 U.S. presidential election.

The Misuse of Data
The heart of the controversy lay in how Cambridge Analytica acquired the data. The firm obtained personal information from millions of Facebook users through a third-party app that collected data under the guise of academic research. However, this data was used for political campaigning, violating Facebook’s policies and raising questions about the platform’s ability to safeguard user information. The scale of the data breach, affecting up to 87 million users, and the sensitive nature of the exploitation for political ends caused global outrage and intense scrutiny of Facebook’s data privacy practices.
Public and Regulatory Response
The revelation of the scandal triggered widespread public concern over privacy rights and the security of personal data online. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide demanded answers from Facebook, leading to hearings in the United States Congress and the United Kingdom Parliament. Facebook’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, was called to testify, facing questions about the company’s data protection measures, its policies on third-party access to user information, and its role in safeguarding democracy from manipulation through social media.
Legal and Financial Repercussions
In the wake of the scandal, Facebook faced significant legal and financial consequences. Regulatory bodies imposed fines on the company for failing to protect user data and for its lack of transparency regarding third-party access to information. The scandal also led to a decline in user trust, prompting Facebook to announce a series of measures aimed at tightening its data privacy policies, restricting third-party access to user information, and improving transparency about data usage on its platform.
Reforms and Policy Changes
Facebook initiated a comprehensive review of its privacy practices and substantially changed its platform to prevent similar abuses. This included removing the ability of third-party apps to access extensive user data, introducing more transparent privacy settings for users, and conducting audits of apps with access to large amounts of information. Additionally, Facebook increased its efforts to combat misinformation and foreign interference in elections, investing in more robust security and content review processes.
Legacy
The Cambridge Analytica scandal marked a turning point in public awareness and regulatory scrutiny of social media platforms’ data practices. It underscored the challenges of protecting personal information in a connected world and the potential for data misuse in influencing democratic processes. The scandal has had lasting implications for Facebook and other tech companies, driving a global conversation about privacy rights, the responsibility of platforms in managing user data, and the need for more robust data protection laws to ensure the ethical use of digital information.
Theranos Big Corporate Scandal (2018)
Theranos, once a Silicon Valley sensation, promised to revolutionize the healthcare industry with a technology that could conduct a wide range of tests using just a few drops of blood. Founded by Elizabeth Holmes in 2003, the company attracted significant attention and investment, boasting a valuation of nearly $9 billion at its peak. Theranos formed partnerships with major retailers and was poised to change medical diagnostics with its innovative technology.

The Fallacy
However, in 2015, investigative reports began to surface, challenging the validity and accuracy of Theranos’ technology. These reports revealed that the company’s blood-testing device, the Edison, produced unreliable results and that Theranos was using commercially available machines for most of its tests, contrary to its public claims. The revelation that Holmes and her company had grossly misrepresented the capabilities of their technology to investors, partners, and the public led to a massive scandal.
Theranos Legal and Regulatory Backlash
The fallout from these revelations was swift and severe. Theranos faced investigations from federal agencies, including the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). In 2016, CMS banned Holmes from owning or operating a clinical laboratory for two years, and Theranos began to unravel, eventually dissolving in 2018.
The Trials
Elizabeth Holmes and Ramesh “Sunny” Balwani, the company’s former president, were indicted on multiple charges of wire fraud and conspiracy to commit wire fraud, accused of engaging in a multi-million dollar scheme to defraud investors, doctors, and patients. The legal battles highlighted not only the alleged fraudulent activities but also raised questions about the culture of secrecy and intimidation at Theranos, the role of media and investors in fueling the hype around unproven technologies, and the regulatory challenges of overseeing innovative healthcare startups.
Theranos Impact on the Healthcare and Tech Industries
The Theranos scandal profoundly impacted the healthcare and technology sectors, prompting increased scrutiny of startups claiming to offer groundbreaking medical technologies. It underscored the importance of due diligence, the need for transparency in scientific claims, and the ethical responsibilities of companies in the healthcare industry. The scandal also served as a cautionary tale about the dangers of hype and the cult of personality in Silicon Valley, where ambitious claims and charismatic founders can sometimes overshadow the rigorous validation of the technology.
Theranos Legacy
The legacy of Theranos and Elizabeth Holmes is a complex narrative about ambition, innovation, and the fine line between vision and fraud. It has become a case study in ethics, corporate governance, and leadership responsibilities. The Theranos scandal continues to resonate as a reminder of the critical need for integrity and transparency in pursuing technological and entrepreneurial success.
How can big company scandals Shake share prices?
As seen in cases like Enron, Volkswagen, and Theranos, big company scandals can significantly shake share prices due to losing investor trust and confidence in the company’s management and future profitability. When scandals are exposed, they often lead to immediate and sharp declines in stock values as investors sell off their shares to mitigate losses, anticipating regulatory fines, legal costs, and potential long-term damage to the company’s brand and market position.
The uncertainty surrounding the extent of the scandal’s impact, potential regulatory actions, and the company’s ability to recover also contributes to market volatility. In addition to financial penalties, these companies often face increased scrutiny and oversight, which can constrain their operations and affect their growth prospects, further dampening investor sentiment. The erosion of customer trust and potential loss of business can lead to decreased revenues and earnings, compounding the negative impact on share prices. Overall, the revelation of corporate misconduct undermines the fundamental assumptions about a company’s value, leading to a reevaluation of its financial health and prospects by the market.
Conclusion
The corporate scandals involving Enron, WorldCom, Lehman Brothers, BP, Uber, Apple, Facebook, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, Kobe Steel, Equifax, Volkswagen, and Theranos highlight significant ethical, regulatory, and operational challenges in the business world. These cases reveal a common theme of corporate malfeasance, where pursuing profit, growth, or market dominance led companies to engage in fraudulent activities, environmental negligence, or gross mismanagement.
They underscore the profound consequences of corporate actions on stakeholders, including employees, investors, consumers, and the broader public, often resulting in financial loss, legal penalties, and irreparable damage to reputations. These scandals have prompted a global discourse on the importance of transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct in corporate governance. Regulatory bodies worldwide have responded with stricter oversight, enhanced compliance requirements, and more severe penalties for misconduct.
The incidents also serve as cautionary tales, reminding corporations of the long-term value of ethical business practices over short-term gains. They have spurred reforms in corporate governance structures, encouraging companies to prioritize ethical considerations and stakeholder welfare in their operational strategies. Ultimately, these scandals have contributed to a growing awareness and demand for greater corporate responsibility and ethical leadership in the quest for sustainable business success.