Table of Contents
Foreign exchange reserve or foreign reserve refers to the foreign currencies held by the central bank or other countries’ monetary authority. It can be in the form of cash or assets that can be liquidated. There are numerous reasons why maintaining an excellent foreign exchange reserve is essential, the most crucial in safeguarding the local currency’s value.
We are part of a global economy where trade is made beyond boundaries. A country’s foreign exchange reserves depend on its total imports and exports. A local exporter is paid by its trading partner in USD, CAD, Euros, or other currency. The trader deposits this foreign currency into his local bank, and in exchange, he receives local money, which he can use for his day-to-day transactions. The local bank then transfers the foreign currency to the central bank.
How are Foreign Exchange Reserves Accumulated?
Similarly, when a country imports any commodity, it has to pay the other country or the foreign trader in their respective currency. This leads to a decline in foreign exchange reserves. Thus, to accumulate foreign exchange reserves, a country needs to increase its exports and decrease its imports.
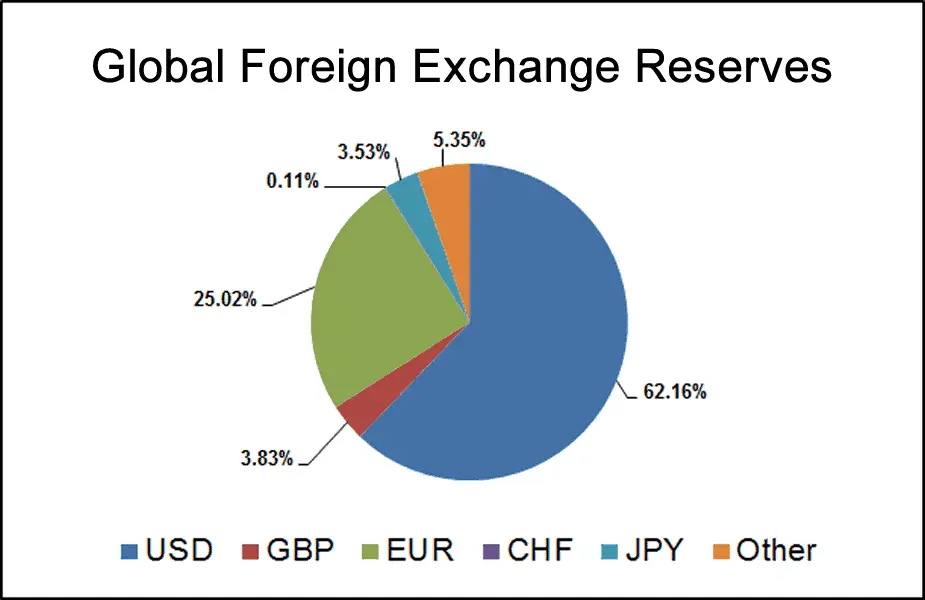
The US dollar’s dominance as a 62.16% global reserve currency can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Stability: The US dollar is seen as a relatively stable currency compared to others, which makes it a popular choice for countries looking to diversify their reserves.
- Liquidity: The US dollar is the most traded currency in the world, making it easy for countries to buy and sell it quickly without disrupting the market.
- Size of the US economy: The US has the largest economy in the world, and many countries trade with the US, making the US dollar an essential currency for international trade.
- Role of the US in the global financial system: The US has a dominant position in the global financial system, with many major financial institutions based in the US, contributing to the popularity of the US dollar as a reserve currency.
- Petrodollar system: The US dollar’s status as a reserve currency is also linked to the petrodollar system, where many countries are required to use US dollars to buy and sell oil, which creates a constant demand for the US dollar.
Overall, the US dollar’s dominance as a reserve currency reflects its stability, liquidity, and role of the US in the global financial system, as well as its link to the petrodollar system.
Why are Foreign Exchange Reserves Important?
The importance of Foreign exchange reserves is based on stability because they ensure that a country’s economy remains stable and resilient in the face of external economic shocks and challenges. Foreign exchange reserves provide a country with a cushion against economic instability and uncertainty, help monetary policy, and attract foreign investment.
These reserves are typically held in foreign currencies, such as US dollars. They can be used to support the value of a country’s currency, stabilize financial markets, and pay for imports in the event of a balance of payments crisis.
Foreign exchange reserves are essential for every nation, including bonds, deposits, banknotes, treasury bills, gold, and other government securities. Foreign Exchange Reserves can ensure that the central government agency has backup funds to support the national currency if it devalues at some point.
The importance of foreign exchange reserves for developing countries is based on the security of home currency positions, economic growth boost, maintaining liquidity in financial crisis, attracting foreign investments, funding infrastructure projects, etc.
Importance of Foreign Exchange Reserves List
- Stability: Foreign exchange reserves help ensure stability in a country’s currency exchange rates by providing a buffer against unexpected fluctuations.
- Trade: Reserves can facilitate international trade by ensuring a country can pay for imports or convert its currency to other currencies for exports.
- Investment: Reserves can attract foreign investment by demonstrating a country’s ability to pay its debts and maintain its currency’s value.
- Crisis management: In times of financial crisis, foreign exchange reserves can stabilize the economy and prevent a currency crisis or default.
- Sovereign credit rating: A country’s foreign exchange reserves are a critical factor in determining its sovereign credit rating, affecting its ability to borrow money and its interest rates.
- Confidence: Holding sufficient reserves can increase market confidence in a country’s economic stability, attracting more foreign investment.
- Monetary policy: Foreign exchange reserves can also help a country’s central bank implement monetary policy by providing a source of liquidity for the banking system.
- Strategic importance: Some countries view foreign exchange reserves as a strategic asset, as they can be used to exert influence or pursue geopolitical goals.
Foreign exchange reserves include banknotes, deposits, bonds, treasury bills, and other government securities. These assets serve many purposes but are most significantly held to ensure that a central government agency has backup funds if their national currency rapidly devalues or becomes insolvent.
Maintaining a foreign exchange reserve is essential for every nation. Whether developing or developed, every country makes calculated moves to ensure that its foreign reserves never see a fall. There are seven reasons why these reserves are essential:
Foreign exchange reserves can Secure the Position of Home Currency
One of the most advantageous positions a country with considerable foreign exchange reserves enjoys is its currency’s security. These reserves maintain the value of the home currency at a fixed rate. Thus, it safeguards the home currency against devaluation. It also promotes sales. For example, China pegs the value of the yuan against the USD. SStockpiling USD raises the dollar’s value compared to the yuan, increasing their sales as Chinese exports become cheaper than American-made goods.
Foreign exchange reserves can Boost Economic Growth.
Some countries with a floating exchange rate system use foreign exchange reserves to keep their currency lower than USD. For example, with its floating currency, the yen, Japan buys U.S. treasuries to keep the yen’s value lower than USD. This encourages exports, that leads to economic growth.
Foreign exchange reserves can Maintain Liquidity in Economic Crisis.
Maintaining a foreign exchange reserve allows a country to import necessary commodities, otherwise not being produced locally due to crises like volcanic eruptions or floods. In such cases, the central bank aids the local exporter by liquidating its foreign reserve. The bank exchanges foreign currency for the local currency, enabling domestic exporters to import essential items.
Similarly, wars, military coups, or political instability can make foreign investors apprehensive about investing in an unstable country. This can encourage them to withdraw their deposits from their bank, creating a foreign currency shortage. This can lead to inflation as imports will become expensive. If a country has enough foreign currency, such situations can be avoided.
Foreign exchange reserves can Attract Foreign Investment.
‘Money brings.’ This statement holds when we are talking about foreign exchange reserves. Every country needs foreign investment for economic growth. The central bank uses foreign reserves as leverage to provide confidence to foreign investors. It assures the investors that their assets will be protected.
Foreign exchange reserves can Meet External Obligations.
The importance of foreign exchange reserves for developing countries is invaluable, but this point is crucial. Countries require foreign currency to settle international payments, including sovereign and commercial debts. In addition, developing countries depend on financing and loans from international monetary authorities. Therefore, if these countries don’t have enough foreign balance, it can reduce their borrowing powers.
Foreign exchange reserves can Fund Infrastructural Development.
The importance of foreign reserves is not limited to financial interaction with foreign countries. Various countries use their resources to fund their infrastructure sector as well. For example, China recapitalized some of its state-owned banks using its reserves.
Foreign exchange reserves can Boost Returns.
To boost returns without compromising safety, many countries hold various interest-bearing investments. This can be in gold, treasury bonds, or other assets easily liquidated.
Critical Points of Foreign Exchange Reserves
- These can be stocked as banknotes, treasury bills, bonds, deposits, and other government securities.
- These are emergency funds for a country in uncertainties like floods, volcanic eruptions, wars, etc.
- USD, the global currency, is the most preferred currency for foreign exchange reserves. China is the leader in holding the highest foreign funds in USD.
- These are required to maintain the local currency’s value, maintain competitively priced imports, and assure foreign investors.
- These are required to maintain a country’s borrowing power and settle international debts.
Why do we need foreign currency?
We need foreign currency because we use currency as a medium of exchange for goods and services, and we need to buy products and services from a foreign country. In addition, the foreign exchange rate helps us convert the price of one currency to another and determine a nation’s economic health.
Ideally, a country must have enough foreign exchange reserves to support three to six months of importing essential commodities like food. In addition, it should have a reserve surplus to settle its debt payments and current account deficit of 12 months. In 2015, when Greece faced economic crises, it used its reserves with the IMF to repay the European Central Bank.
Countries and Foreign Exchange Reserves
Countries with large trade surpluses are at the top of this list. Since their exports are higher than imports, they stockpile dollars.
As of 31st December 2017, several countries have foreign exchange reserves of more than $100 billion, with China being the leading country with a budget of $3,236 billion. Its major export is consumer goods and parts. Japan follows it with budgets of $1,264.0 billion following auto parts and consumer product exports. Saudi Arabia made it to the list by being an exporter of oil. By exporting manufactured goods and chemicals, the United Kingdom has a reserve of $150.8 billion. The United States, too, exports manufactured goods and chemicals. As a result, it has foreign exchange reserves worth $123.3 billion.
Other countries on this list are the European Union, Switzerland, Taiwan, Russia, Hong Kong, India, South Korea, Brazil, Singapore, Thailand, Germany, Mexico, France, Italy, the Czech Republic, Indonesia, Iran, Poland, Israel, Turkey, and Malaysia.
























