Table of Contents
Financial intermediation is a well-known process that most of us are familiar with. For example, financial intermediation happens when a primary lender transfers his funds to the primary borrower. But this process essentially requires two conditions. First, during financial intermediation, the borrower’s securities convert into indirect securities, and the lender’s funds convert into an indirect fund. Thus, financial intermediaries are considered the backbone in forming the basic structure of indirect financing. Here, the person borrowing the money accesses financial help through them a loan from the financial market.
What is indirect finance?
Indirect finance is when borrowers borrow funds indirectly from the financial market (such as banks) rather than directly from investors.
What is the indirect finance market?
An indirect finance market represents a financial market such as banks, insurance companies, credit unions, etc., where borrowers can borrow money instead of asking for money from investors.
Indirect finance examples
One example of indirect finance is when a financial institution, such as a bank or credit union, works with other companies to provide consumers with financing options for big-ticket items like cars or houses. For example, a consumer may go to a dealership to buy a new vehicle and apply for an auto loan through the dealership’s lending partner. The lending partner then uses this application to determine whether the consumer is eligible for the loan and what interest rates they will be charged.
Another common type of indirect finance involves peer-to-peer lending platforms, which connect individual borrowers with investors looking to invest in various loans. For example, individuals may use these platforms to seek funding for their small businesses or cover unexpected medical expenses. In many cases, lenders on these platforms are interested in earning a return on their investment rather than seeking long-term returns from interest payments that borrowers make over time.
Indirect finance is also used by institutional investors such as pension funds or mutual funds that purchase company securities or pass through debt obligations issued by municipalities or sovereign governments. These investments typically involve large amounts of capital. They are often purchased on secondary markets where investors can buy pre-existing securities from previous issuers at attractive prices relative to their face value. Indirect finance has become an essential tool for institutional and individual investors in managing risk exposure and enhancing portfolio performance in volatile financial markets.
The list of financial intermediaries providing indirect financing is as follows:
- Banks
- Building societies
- Collective investment schemes
- Cooperative societies
- Credit unions
- Financial advisers or brokers
- Insurance companies
- Mutual savings banks
- Pension funds
- Savings banks
- Stock exchanges
Indirect finance example: The client deposits funds into a checking account in the bank. Bank uses the money to make a loan to a fellow student.
Indirect loan as indirect finance
An indirect loan is an installment loan involving the lender having a relationship with a third party instead of directly with the borrower. This can take two forms: either a company offering a loan to the consumer, who then sells it to a bank, or the company accepting a loan from the consumer and processing and originating it for the bank.
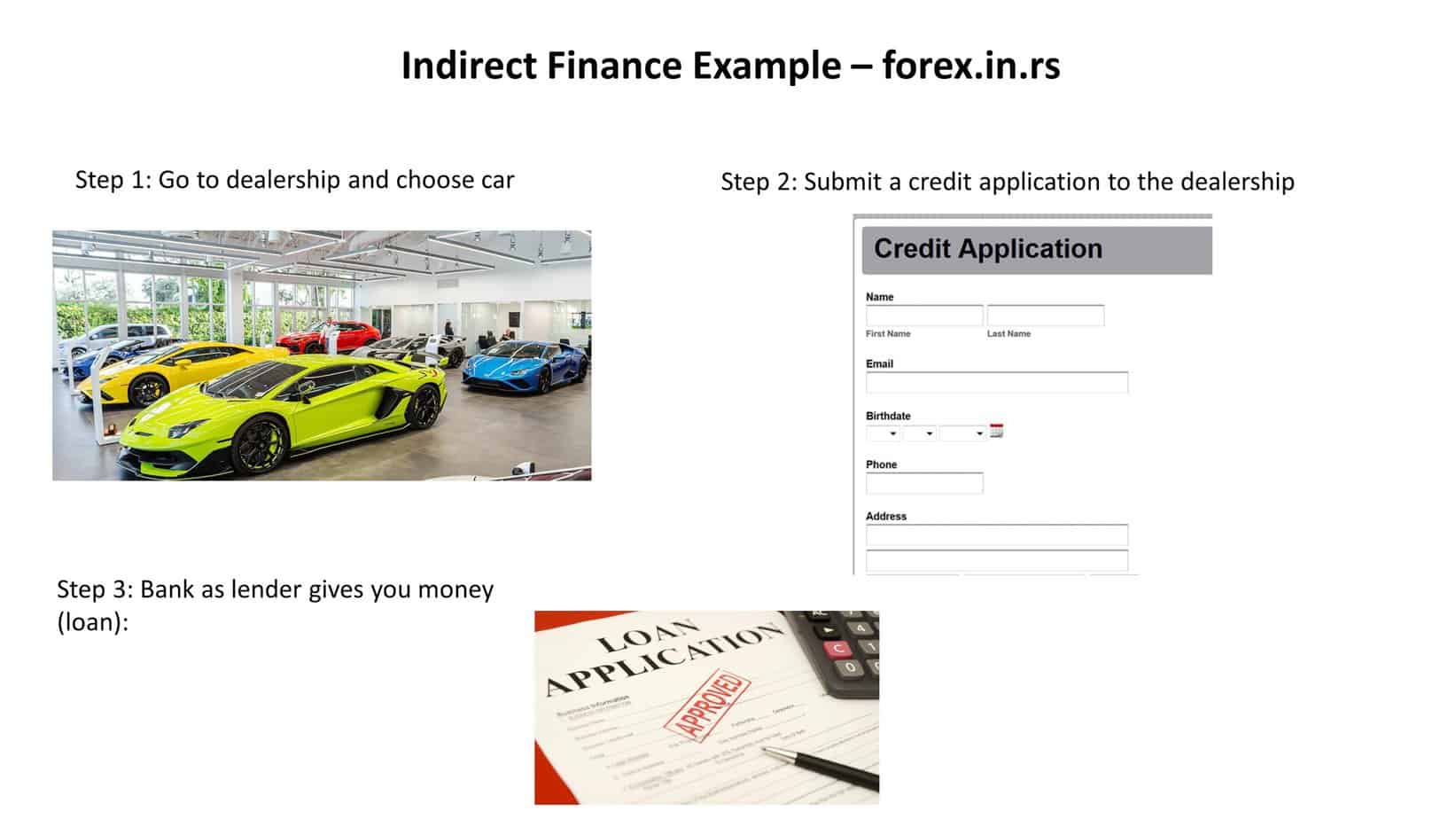
One typical example of an indirect loan is an auto loan from a dealership. When you apply for an auto loan through a dealership, your credit application may be sent to multiple lenders in their financing network. This allows you to find your situation’s best terms and interest rates. The dealer can also forward your application directly to the bank, which will fund your loan.
Indirect loans are appealing because they offer borrowers more options when finding financing for their purchases and potentially lower interest rates than they would get if they applied directly with a lender. However, these loans can also carry higher fees and other costs, so it’s essential to research and ensure you understand all of the terms before signing on to an indirect lending arrangement.
For instance, a small business entity doesn’t approach any investor directly. Instead, the well-known source of borrowing money is a loan from a bank. First, the bank provides a loan to the business and charges a particular amount as interest. Then, the bank uses this interest to pay its interest amount to the investors and ordinary depositors.
Direct vs. Indirect finance
What is the Difference Between Direct and Indirect Financing?
While direct financing borrows money directly from the lender, indirect financing implies borrowing money using intermediaries. There is only one financial instrument between the borrower and the lender in direct funding, while indirect financing consists of two different instruments.
What does the word ‘financing’ mean? Financing is putting your money as a fund for business entities, investing in other firms, or simply putting your money for important business purchases. Financing can be of two types: direct and indirect financing. Equity financing, purchase of securities, or credit arrangements in bonds and stocks are commonly seen in funding activities. These methods are considered a few forms of direct financing.
In direct financing, a business is not adhered to paying any interest rate. In these methods, generally, the investor lends his money directly to the borrowers with brokers, dealers, or even investment banks.
Indirect financing by financial intermediaries is the most critical concept when you opt for indirect financing. These intermediaries play vital roles in purchasing direct claims from the borrower, along with a particular set of parameters. Then they convert these direct claims with a different set of parameters to propose to the lender for selling purposes. This is the most common indirect financing example seen across businesses.
The main difference between these two types of financing is the number of financial instruments involved. In direct funding, there is only one financial instrument between the borrower and the lender. But indirect funding consists of two different instruments in the presence of intermediaries. The first is between the lenders and the intermediaries, and the second is between the intermediaries and the borrowers.
Indirect finance advantages
- Indirect finance is a quicker way for businesses to raise money.
- Indirect finance allows businesses to search for multiple loan opportunities at once.
- indirect finance includes more parties
- Favorable interest rates
- You keep complete control of your company
The effective participation of financial intermediaries in indirect financing has become popular across businesses. The intermediaries take all the responsibilities, from approaching the investors to checking and completing the required process. In this way, companies can raise more money in lesser time with no direct involvement. The financial intermediaries have been working very efficiently in reducing the information cost related to money lending. They are also very quick with the asymmetrical information problem at a meager price. Economies of scale and expertise are crucial to make it cost-effective. Not only that, the intermediaries provide critical financial services as well. Indirect financing advantages include the following:
1. Maturity Transformation and Denomination
When a company wants to raise a whopping amount of money, for example, $400 million or more, it is impossible to get help from retail investors. In these cases, the bank appears as a savior by sanctioning a loan for the company. The bank can issue the loan by accumulating the savings money of thousands of small and medium deposits and give a massive loan to the company,
That’s not all. The bank can also issue a confidential long-term loan. Once these reach their maturity date, two things can happen to the deposit; they can get renewed, or a different scheme will replace them. These processes are very beneficial for businesses to get sustainable liquidity.
2. Risk Diversification:
Financial intermediaries are experts considering their investment in multiple loans simultaneously. The money that the depositors put into the bank can be deployed across a vast portion of the borrowers. Pooled funds diversify associated risk as they are put into many different instruments. Popular financial intermediaries such as mutual funds or commercial banks usually have risk management experts who are very resourceful. The risk management team looks after alternative investments’ risk and return ratios and suggests necessary actions. This is why banks can guarantee a safe deposit and always return the depositor’s money even when it has to go through a loss.
Although these factors are considered the advantages of indirect financing, these can turn into disadvantages. There are several high-scale costs, such as brokerage commissions. These costs can be reduced per unit but only at a certain point. After that, the fixed costs will be active again. The most significant disadvantage of indirect financing is the spread offered by the intermediaries.
All You Need to Know About Financial Intermediaries
The intermediaries’ main work is to invest the savings and investments of their customers and lend money to individuals or invest in companies to get returns. The difference between their earnings through asset lending and their payback to the customers as liabilities is their profit. In their case, the assets are the loans, bonds, or stocks, and the liabilities are the customer deposits and any other form of the invested money. There are generally three branches of this institution. They are as follows.
- Depository institutions
The famous depository institutions are commercial banks, credit unions, savings and loan associations,s and mutual funds. These institutions generally take their customers’ deposits as savings or investments and lend them to the borrower. The most commonly viewed intermediary, the commercial banks, raises the loan amount through savings or issuing checkable and time deposits. On the other hand, credit unions are all about deposits in the form of shares. Typically, these shareholders are the member or employees of an organization.
Commercial banks can primarily raise funds through saving deposits, time deposits, checkable deposits, and credit union deals, including shares as deposits. Generally, employees or members of an organization hold these share accounts.
- Contractual Savings Institutions
The most familiar contractual savings institutions are life insurance companies, pension funds, or retirement funds provided by the government. These type of intermediaries get their hands on funds at periodic intervals. Working entirely based on a contract, these institutions work under specific conditions. The agreement includes certain events when the payroll will be necessitated. Whereas the insurance companies get the fund through premiums paid by the policyholders, pension funds work with retirement benefits in an annuity. Both insurance companies and pension funds invest in corporate mortgages, bonds, and stocks. Policyholders must pay a premium to the insurance companies to keep their policies running. These premiums act as funds for insurance companies. These policyholders also buy mortgages and bonds. Retirement benefits are reaped from pension funds as an annuity. Some policyholders invest in stocks and bonds as well.
- Investment Intermediaries
Mutual funds and finance companies fall under this category. These entities issue and sell their company’s shares and later invest the proceeds in a different, diversified portfolio of securities. The funds include corporate bond funds, stock mutual funds, money market mutual funds, and mortgage-backed security funds. In addition, the hedge fund, which is only accessible to accredited investors, is also included in this category.
Although commercial bank always has the edges for being the largest indirect investment source, hedge funds and insurance companies are not far behind. These three, altogether, are the largest source of financial help for businesses across the globe. With these indirect finance methods, small and medium-sized businesses are becoming a significant source of the economy. These intermediaries rule it for indirect finance without substantial marketable debt and equity security clauses.
























