Table of Contents
Volatility and high returns go hand in hand. Assets are property or something that is of value. There are different types of intangible and tangible things that are assets. However, in the trading and investing world, there are different classes of assets. The volatility of an asset is a massive concern for those who trade or invest capital. The prime variance of the asset is volatility over time. The higher the volatility, the wider the price ranges in terms of the long-term period. There are more volatile assets than others, and what makes a market attractive or unattractive is the variance of the market, as different investors have different risk profiles.
One of the most important factors for considering which asset to trade or invest in is the asset variance.
If you want to trade commodities, please visit the commodities trading page.
What are Commodities?
Commodities trading assets refer to raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold, such as gold, oil, or wheat. They are typically standardized and interchangeable with other goods of the same type, and they are traded on various exchanges or in the over-the-counter market.
All commodities are assets, but not all assets are commodities because assets are wide-term.
Generally, commodities are financial assets defined as any good or service bought and sold purely on price. Usually, when we say commodity, we think of raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold, such as copper or coffee.
To understand commodities, one needs to understand what they entail, considered raw materials used to create consumer goods such as aluminum, silver, gold, natural gas, oil, wheat, and cattle. They are, in almost every industry, referred to as commodities. One can also find soft commodities stored for some time, such as coffee, cocoa, cotton, or sugar.

From the beginning of time, the commodity market has evolved considerably ly. There used to be a time when farmers would store apples and then sell them in the market if the prices increased. Then, during the 19th century, the demand grew for standardized contracts to ensure that the commodity prices could be fixed or agreed upon. Therefore, the development began of the commodity futures exchange.
These days, options and futures contracts are easily traded on different exchanges in various parts of the glove and deal in various energy, metal, and agricultural products and soft commodities. The price risk is offloaded to the end-users due to the standardized contracts, and it helps the commodities producers’ significance at the end of the 20th century, com rapidly changed as an asset class. The commodity futures indexes were developed, as well as the benchmark of the indices with the investment vehicles. Ncanopportunity to select from a range of vehicles to invest in the futures market of commodities, from notes to mutual funds or exchange-traded funds, which cover the vast spectrum from broad-based commodity single-based single and even sector-based commodity exposures.
What are the most volatile assets?
Commodities such as lithium, oil, and cotton are the most volatile assets because price has fluctuated in a more extensive range in the last several decades because of demand fluctuations. Additionally, sometimes cryptocurrencies can be more volatile than commodities because of the thin market, speculative nature, and regulatory news.
Volatility measures how much the price of a commodity fluctuates.
The volatility of commodities, such as lithium, oil, and cotton, has increased significantly in recent years due to a combination of factors. First and foremost, commodities are directly impacted by global supply and demand dynamics. Factors like geopolitical tensions, environmental changes, and technological advancements can cause sharp and sudden changes in the availability or demand for these resources. For example:
- Lithium: As the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) has surged, so has the demand for lithium, a primary component of EV batteries. Any disruptions in supply or new technology advancements can lead to significant price volatility. Oil prices can swing based on geopolitical tensions, production changes by major oil producers, and global demand shifts, such as those caused by economic cycles or shifts toward renewable energy.
- Cotton: Weather conditions, which are increasingly unpredictable due to climate change, can significantly impact cotton crops. Trade tensions can also influence prices.
The volatility percentages you provided further showcase the heightened fluctuations in commodity prices. These high percentages indicate that the prices for these commodities have experienced significant changes within a specific time frame.
Furthermore, you’ve mentioned cryptocurrencies, which can indeed be very volatile. Their volatility often stems from factors like regulatory news, technological developments, market sentiment”, and the relatively minor market compared to traditional assets. This “thin market” can lead to sharper price movements as larger trades have a more pronounced effect on the overall market price.
In summary, commodities and cryptocurrencies are subject to a myriad of factors that can cause their prices to swing significantly, making them more volatile than other asset classes like equities or bonds in many instances.
Commodity volatility statistics
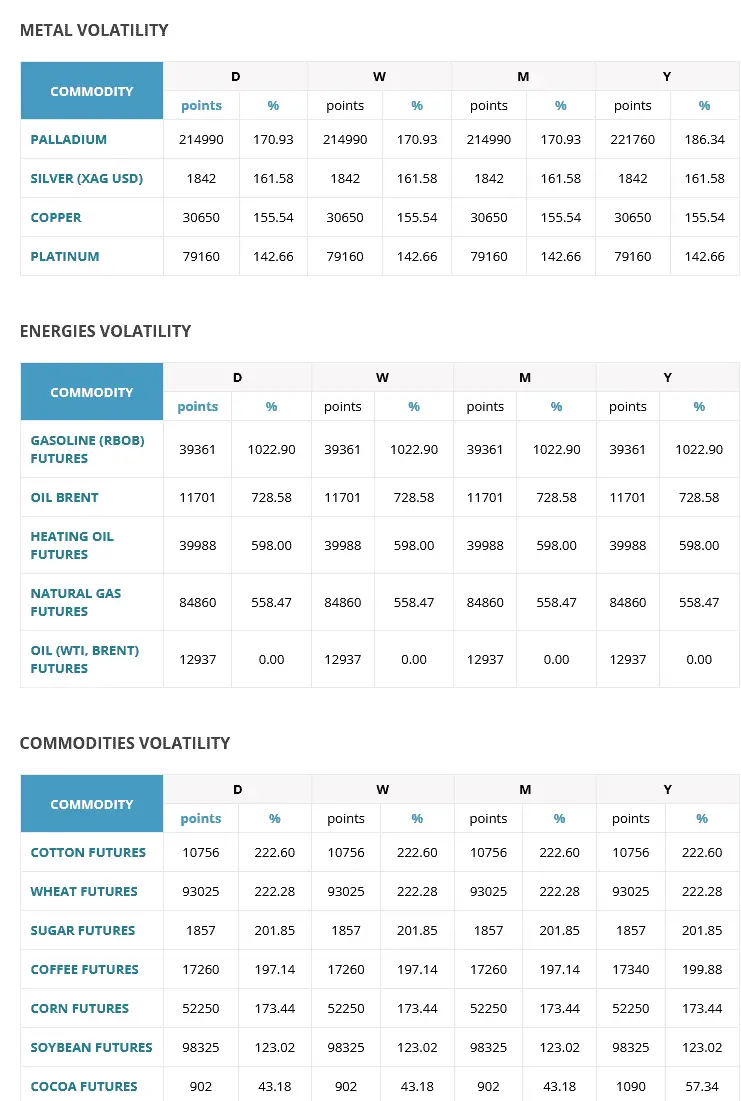
Let’s break down the volatility of these commodities based on the data:
- GASOLINE (RBOB) FUTURES: A change of -39,361 points represents a massive shift, with a volatility rate of 1022.90%. This suggests that the price of gasoline futures experienced an extreme fluctuation, potentially due to factors like geopolitical issues affecting oil-producing regions, refinery outages, or significant shifts in demand due to economic factors.
- OIL BRENT: With a shift of -11,701 points and a volatility rate of 728.58%, oil prices also underwent a notable change. Oil is sensitive to global supply and demand dynamics. Factors like OPEC decisions, geopolitical tensions, technological breakthroughs, and global economic health can lead to significant price swings.
- HEATING OIL FUTURES: The change of -39,988 points, a volatility of 598.00%, indicates that the heating oil market was also considerably volatile. Heating oil prices are influenced by crude oil prices, refinery capacities, and seasonal demand, especially during colder months in regions dependent on heating oil.
- NATURAL GAS FUTURES: With a change of -84,860 points and a volatility of 558.47%, natural gas prices showed significant movement. Natural gas is sensitive to factors like production levels, storage capacities, weather patterns (which influence demand for heating and cooling), and technological advancements in extraction techniques.
- COTTON FUTURES: A change of -10,756 points and volatility of 222.60% suggests that cotton prices also experienced notable fluctuations. Cotton can be influenced by factors like global production levels (affected by weather patterns), demand from major cotton-consuming industries, and trade dynaEach
These commodities witnessed substantial price shifts, as shown by the point changes and percentage volatilities. These movements can be attributed to a complex interplay of global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical tensions, environmental factors, and technological changes, among other factors. The sheer magnitude of these changes underscores the inherent volatility of commodity markets.
Why are commodities volatile?
Commodities are volatile for various reasons, often stemming from supply and demand dynamics, as well as external influencing factors. Here’s a breakdown:
- Supply Constraints: The production of commodities can be influenced by various factors:
- Natural Disasters: Events such as droughts, floods, hurricanes, and other extreme weather events can severely affect the production of agricultural commodities and disrupt mining or drilling operations.
- Geopolitical Events: Wars, sanctions, and political instability in key producing regions can disrupt supply.
- Regulation and Policy: Government policies related to environmental concerns, land use, or trade can influence production levels.
- Demand Fluctuations:
- Economic Growth: As economies grow, especially in emerging markets, the demand for raw materials and energy often increases.
- Technological Changes: Advances in technology can increase or reduce demand for certain commodities. For instance, the rise of electric vehicles impacts the oil demand and increases the demand for minerals like lithium and cobalt.
- Seasonality: Some commodities, like natural gas or heating oil, have seasonal demand patterns due to weather changes.
- Speculation: The commodities markets attract a lot of speculative trading, which can amplify price movements .ulators often trade based on forecasts or news, leading to short-term price volatility.
- Limited Storage: For some commodities, especially perishables like agricultural goods, there are limits to how much can be stored. If the suction exceeds storage capacity, prices can drop sharply. Conversely, if there’s a shortage and storage is low, prices can spike.
- Inelasticity: In the short both supply and demand for commodities can be inelastic. This means that minor disruption in supply and a slight increase in demand can lead to significant price changes.
- Currency Strength: Commodities are often priced in U.S. dollars. Therefore, the strength or weakness of the dollar can influence commodity prices for global traders.
- Global Markets: Commodities are influenced by events from around the globe. A production issue in one part of the world can affect prices everywhere, making them wider unpredictable events.
- Alternative Products: The emergence or decline of alternative products can influence demand. For instance, as renewable energy sources become more popular, they might affect the demand for coal or oil.
Why are cryptocurrencies volatile?
Cryptocurrencies are volatile due to a” thin market,” which means limited liquidity with fewer buy and sell orders. This limited order depth means that even minor trades can cause significant price swings. Many participants in the crypto market are speculative traders, reacting swiftly to short-term events or sentiments.
Additionally, compared to traditional assets, cryptocurrencies have a relatively short history prediction, and predictions based on past data are more” challenging” and ongoing. Moreover, a small number of large,” referred to as “whales,” can negatively influence the market. This combination of factors, including the market’s shallow depth and speculative nature, leads to pronounced price fluctuations in cryptocurrencies.
Why Should One Invest in Commodities?
The commodity market is vast, and it offers some of the best risk-free returns due to its nature. It is a hedging tool when the inflation rate is unpredictable, dairying by the day. There are three main benefits for investors if they invest in commodities: return potential, diversification, and inflation protection. These three are vital for a robust portfolio.
As commodities are just tangible assets, they would reach different economic changes than bonds and stocks, or financial assets as they are referred to. For example, we know that commodities tend to profit from the rise in inflation and are only rare asset classes. Furthermore, the price of the services and goods increases as their demand increases, and so will the price of the commodities, almost in unison with the changes in demand. Since the commodity price rise accelerates, it may be best to invest in commodities to hedge against inflation.
On the other hand, bonds and stocks perform better when inflation is slowing or stable. When the rate of inflation rises fast, it leads to the lowering of future flow flows that are paid by bonds and stocks, as the future cash would only be able to buy fewer services and goods than today.
What are the most volatile futures?
Some of the most volatile futures in the ten years based on standard deviation volatility are:
- Bitcoin futures 200%
- Crude and WTI Oil: 29.9%
- Copper 20%
- Cotton 18%
- Gold 15%
Let us see the market analysis. The commodity index of Goldman Sachs, Credit Suisse, and Bloomberg has been independent primarily from bond and stock returns in the past and only correlated positively to inflation.
If we look at the period from 1970 to 2015, the annual returns had a low correlation with the U.S. equities on the Bloomberg Commodity Index, and there was a correlation close to zero with the global bonds. They were, however, positively correlated to the US CPI.
Even though the correlation of equities to commodities experienced a pickup after the global financial crisis, it resulted from the decrease in total demand, which impacted many asset classes and resulted in a higher correlation between the two. However, since the period, commodities are responding once again to supply factors. Due to geopolitical instability, the weather impacts the price of grains and even natural gas and doesn’t influence mining or crude oil strikes, which impact metals. The factors don’t affect the bond or stock market r, even more importantly, to a similar degree, and the correlation between other asset classes and commodities has come down.
The low correlation of commodities to bonds and stocks shows the primary advantage of exposure: diversification. For a diversified portfolio, the asset classes move in sync with one another; this leads to a reduction in the overall portfolio’s volatility. The consistency of the returns would be necessary over time due to the lower volatility reducing the portfolio risk. Losses can’t occur even with diversification.
Let us compare commodities, equities, bonds, and forex volatility :
Here is the little test for the last 30 days. Let us take the ADX indicator to measure volatility. Let us picture the ten most volatile assets in the last 30 days.
Here is my small test :

How Can One Invest in Commodities?
It might have been challenging to capture all of the advantages of commodity exposure in the past. Investors have been provided with another option due to investment vehicles benchmarking with commodity futures indexes and gaining exposure. Commodity exposure helps manage against a diversified index. Asset allocation has been done since the beginning of time, which shows that it is beneficial.
Are there any Risks?
Although diversified commodity exposure does offer various advantages, there are risks to commodities investment. During cyclical downturns, commodities might not perform well, and if the industrial and consumer demand slows, other things could impact it, such as politics, natural conditions, and the market.
One more thing. We see in this text that commodities are VolManysets. Many people think that volatility is a bad thing, something like a huge risk. No risk and volatility are different things, and volatility can be a massive advantage in trading. Just try!
If you want to trade commodities, please visit the commodities trading page.
























